Systenic Info
HYPERTENSION
What is hypertension?
Popularly known as High Blood Pressure, Hypertension can lead to severe health complications by increasing the risk of cardiovascular diseases such as stroke, heart attack and heart failure, sometimes even leading to death. It is important to keep your blood pressure under control in order to preserve your health and avoid such complications.
Hypertension Symptoms
Symptoms in hypertension are not always visible and thus it gets it’s other name “the silent killer”. If not diagnosed at a certain level, it can create high complications such as heart ailments; damage to blood vessels and also harm the kidney.
In severe cases, symptoms such as anxiety, sleep issues, heavy sweating and hot flashes might take place. However, this is very rare and most people with this condition do not really experience any symptoms.
In extreme cases where it leads to hypertensive cases, the affected might have headaches and nosebleeds.
Risk factors
Some risk factors caused due to hypertension are:
- Age: With age, the risk of blood pressure also increases. Men are likely at the risk of high blood pressure earlier in age than women.
- Race: African heritage is studied to be at the risk of high blood pressure as opposed to the whites.
- Family history: High BP could also be Hereditary.
- Being overweight or obese: The heavier you weigh, the more blood you require in order to supply oxygen as well as nutrients to your tissues. The more blood circulated through your blood vessels; there is an increase of pressure on your artery walls.
- Not being physically active: Your heart rate would be higher if you are inactive. In this case, the heart needs to function harder with each contraction.
- Using tobacco: Smoking or using tobacco in any form directly increases your blood pressure temporarily. However, the chemicals present in them can have a long-term effect on your artery walls, causing your arteries to narrow which in turn increases your risk to heart diseases.
- Too much salt (sodium) in your diet: The sodium levels in your body can affect the fluid levels, which may increase of decrease your blood pressure.
- Drinking too much alcohol: Alcohol has a direct relation to heart conditions. It is important to drink in moderation if consumed regularly. While men can take up to 2 glasses a day, women should restrict themselves to one.
- Stress: Stress is often directly related to be an underlying cause of high BP. A lot of people rely on food, alcohol and smoking in order to ease their stress, however, one should remember that they are causes of high blood pressure as well.
- Certain chronic conditions: Kidney ailments, diabetes and certain other chronic diseases could also be underlying causes of high blood pressure.
Causes of Hypertension
Hypertension is often caused due to an underlying health condition, while it is not very specific. If an underlying condition is the cause of an increase of your blood pressure, it is called secondary hypertension. The causes of hypertension can depend on the type of hypertension; primary or secondary.
Multiple factors could result in primary hypertension causes that may include:
- High volume of blood plasma
- Hormonal activity level in people with blood pressure
- Stress or the lack of regular exercise
The cause of secondary hypertension is very specific and is a complication of an underlying disease or health issue. The chronic kidney disease is one the most common cause of high levels of blood pressure. This is due to the fact that the kidneys don’t filter out fluids from the body anymore, leading to hypertension.
Some common conditions that can lead to hypertension include:
- Diabetes
- Kidney diseases
- Pheochromocytoma, a rare form of cancer in the adrenal gland
- Cushing syndrome caused by corticosteroid drugs
- Congenital adrenal hyperplasia
- Hyperthyroidism
- Hyperparathyroidism
- Pregnancy
- Obesity
How is hypertension diagnosed
One important way to detect hypertension is to check your blood pressure often. Doctors may be able to check and provide hypertension treatment if you have been hypertension diagnosed.
Doctors may take multiple readings throughout the day in order to diagnose whether you have hypertension or not. This is due to the fact that our blood pressure levels may vary throughout the day.
Hypertension Treatment
A combination of medicinal intervention and lifestyle changes is the treatment provided for hypertension.
With regards to medication, doctors may prescribe tablets based on the underlying condition that caused hypertension in the first place. Some of the common medications are Diuretics, Beta-blockers, ACE inhibitors and vasodilators. These are generally prescribed in more severe cases depending on the root of the problem.
Consequently, doctors will also advice a healthy lifestyle such as nutritious diet, regular exercise and stress-busting activities as a part of your treatment. It is also important to cut down on any alcohol practices and smoking habits that you may have in this case.
Hypertension prevention
Balancing a healthy lifestyle is the best way to prevent hypertension for anyone. Few simple ways to create a healthier lifestyle are:
- Eat nutritious food – eat healthful, add a lot of protein and veggies to your diet.
- Exercise – spend at least 30mins a day exercising. Be it walking, jogging, dancing, cycling or any kind of movement.
- Meditate – meditating every day will help you relax and avoid stress by managing situations calmly.
High Cholesterol
1.What is High Cholesterol?
Cholesterol is a waxy, fat-like lipid that is produced in the liver naturally. It is essential as it is needed for the production of certain hormones, cell membrane formation, and Vitamin D. The food we eat contains cholesterol, hence its presence at normal levels is good for the body. But if the levels are too high it can put a person at a high risk of heart diseases. Different types of cholesterol are, HDL or good cholesterol and LDL or bad cholesterol. The HDL levels should be high and the LDL levels should be low. When the LDL levels are high it is termed as high cholesterol.
High Cholesterol Symptoms
High cholesterol is a silent killer and does not show any symptoms. In many of the cases where high cholesterol is not detected, it leads to emergency events like a stroke or a heart attack. But these events happen only when the arteries are blocked by plaques. These result in the narrowing of the blood vessels and cause complications.
The only way to know if a person has high cholesterol is to get regular check-ups. Blood tests are enough to know the levels of this lipid. Get your cholesterol checked every 4 to 5 years after you reach 20 years to know if the levels are in the normal range.
2.Who is at Risks?
High cholesterol risk factors that are uncontrollable are:
- A person with a family history of high cholesterol is at a higher risk of this condition.
- A woman after menopause is likely to have a higher bad cholesterol level and hence has a risk of heart disease.
- Men over the age of 45 and women over the age of 55 have high chances of high cholesterol thus at risk of heart diseases.
Controllable risk factors are:
- Diabetes or high blood pressure patients
- Being overweight or obese
- Following unhealthy food habits
- Lack of physical exercise
- Smoking and consumption of alcohol.
3.High Cholesterol Causes
Having certain types of high cholesterol raises the chances of having a heart attack or heart disease. When there is high LDL, the fat starts to deposit on the walls of the arteries, narrowing it and restricting the movement of blood. When the blood flow is restricted, it can lead to many serious complications. Things that cause high cholesterol are:
- Consuming foods like meat, cheese, etc in high quantities
- Consuming saturated fats that are present in fried, processed, baked foods. It is also present in dairy products, chocolate and meat.
- Intake of trans fats through fried and processed foods.
- People who have an inherited condition called familial hypercholesterolemia have high LDL.
- Obesity or excess weight
- Drugs like corticosteroids, progestins, etc
- PCOS, diabetes, kidney or liver disease
- Underactive thyroid
4.How is High cholesterol diagnosed?
High cholesterol shows no symptoms and hence everyone who has reached the age of 20 and above should get a high cholesterol test once every few years. That will help them to know the levels and reduce them in case it is high. A simple blood test called the lipid profile is enough for High cholesterol diagnosis and to assess the levels of cholesterol. It helps to determine the LDL, HDL, triglycerides level, and total cholesterol level.
After the test is performed the High cholesterol doctor will do a physical exam by checking the heart rate, blood pressure, and heartbeat. If the doctor finds that the patient is at risk of heart disease further tests are asked to be performed. That includes EKG, stress test, Echocardiogram, tilt table test, and more.
5.How is High cholesterol treated?
High cholesterol treatment depends on the risk factors after which High cholesterol cure is recommended by the doctor:
- Medicine for high cholesterol which helps to keep the levels of cholesterol to a normal range. That aids in preventing other complications that leads to heart diseases and heart attack.
- Lifestyle changes include cutting down on foods that contain high amounts of saturated and trans-fat. Reducing body weight and adopting a healthy lifestyle of exercise and nutritious diet.
- Adding more plant stanols and sterols which keeps the HDL in normal levels and reducing LDL.
6.How can High cholesterol be prevented?
High cholesterol that is genetically inherited cannot be controlled, but High cholesterol prevention is recommended.
- Following the dietitian’s instructions on food
- Consuming a diet that is nutritious with low animal fat, saturated or trans-fat.
- Include omega 3 fatty acids in your diet by including nuts like walnut, flax seeds, and salmon, trout, and sardines.
- Limiting consumption of fried, processed and sugary foods
- Avoid smoking and consuming too much alcohol.
- Avoid smoking
- Exercise especially aerobic for at least 3 to 4 times a week.
- Maintain a normal weight
- Take medications regularly
- Follow recommendations of regular cholesterol checks if you are at risk of heart disease.
Diabetic Kidney Disease
What is Diabetic Kidney Disease?
A high percentage of people with diabetes (Type 1 & 2) end up with some damage to their kidneys. This condition, also known as diabetic nephropathy, occurs when the nephrons in the kidneys work overtime in expelling glucose from the blood. When the blood sugar levels increase frequently, they also damage the blood vessels in the kidneys. This is a serious and life-threatening condition and is usually progressive if not treated actively.
What are some Common Symptoms of Diabetic Kidney Disease to watch out for?
Diabetic kidney disease may not have any symptoms in its early stages. Or they may be indistinct and vague like feelings of tiredness and having low energy. And when the symptoms do start occurring with a decrease in the functioning of the kidneys, they are different for everybody depending on the severity of the damage, age of the patient, and the general health.
Some of the most common symptoms include-
- Inability to think clearly and lack of coordination
- Not feeling hungry.
- Constant high blood pressure.
- Itchy and dry skin.
- Cramps in the muscles.
- Swollen ankles and feet due to water retention.
- Puffiness around the eyes.
- Frequent urges of urination.
- Constant feelings of nausea and vomiting.
- Pallor.
- Reduced need for insulin or diabetes medicines.
- Shortness of breath.
- Feeling of fatigue.
What Causes Diabetic Kidney Disease?
While the exact reasons for diabetic kidney disease are unknown, there are some reasons that are known to contribute actively. It’s good to know some of the most common causes and risk factors of diabetic kidney disease that include:
- People who are of American-Indian, Hispanic, or African-American descent.
- People who have a family history of kidney diseases.
- People who have developed Type-1 Diabetes before the age of 20 years.
- Smoking
- Overweight people are more prone to diabetic kidney diseases.
- Co-existing diabetic conditions like nerve damage or eye diseases.
- People who suffer from high blood pressure and high cholesterol levels are more prone to this condition.
How is Diabetic Kidney Disease Diagnosed?
If you suffer from diabetes and have been experiencing the above-mentioned symptoms, it is essential to talk to your doctor. Once the doctor understands these and assesses your medical history, she/he may refer you to a nephrologist or an endocrinologist and suggest these tests.
1. Blood & Urine Tests
These are the most common tests to check for early signs of damages to the kidney. These tests are also good indicators of the working condition of the kidneys and the presence of microalbumin protein or urea nitrogen in the urine and the blood.
2. Imaging Tests
An X-Ray, CT-KUB, MRI, or ultrasound may be done to assess the structure and size of the kidneys and determine how well the blood is circulating in the kidneys.
3. Renal Analysis
This test is done to analyse the kidneys’ filtering capacity and functioning.
4. Biopsy
This may be done to closely examine the tissues of the kidney and check their functioning.
What are the Complications from Diabetic Kidney Disease?
- Pulmonary edema
- Hyperkalemia (increase in the potassium levels of the blood)
- Stroke
- Diabetic retinopathy (damage to the blood vessels in the retina)
- Heart diseases
- Anaemia
- Foot sores
- Complications during pregnancy to the mother and the child both
- Persistent diarrhoea
- Damaged nerves and blood vessels
- The most common and serious complication is irreversible kidney damage and kidney failure.
How is Diabetic Kidney Disease Treated?
Since diabetic kidney disease is an irreversible condition and cannot be cured, treatments are used to curtail its progression. This is done by managing your blood sugar levels and hypertension to slow down or delay its progression and other complications. The treatment depends on the stage of diabetic kidney disease that you are in and include:
1. Early Stage
Medications: Your doctor may administer medicines to control your high blood pressure, high blood sugar levels, bettering your bone health, and controlling the levels of proteins in urine.
2. Advanced Stage
Kidney Transplant: A kidney transplant includes placing a kidney from a donor in your body to help treat chronic kidney disease and help you feel better and live longer.
Dialysis: Dialysis helps in removing waste, salt, and extra water from building up in the body and to control high blood pressure levels. Depending on your condition, your doctor will advise haemodialysis or peritoneal dialysis.
How can one Prevent Diabetic Kidney Disease?
There are several diabetic kidney disease guidelines that can not only prevent this condition but also slow down its progression. Ways in which you can keep your kidneys healthy for long include:
- Managing your diabetes to help in preventing or delaying diabetic kidney disease.
- Be physically active and incorporate at least 30 minutes of exercise in your daily routine. This helps in not only losing weight but in also reducing high blood pressure.
- Quit smoking.
- Keep your blood sugar levels within a permissible range.
- Manage your blood pressure and avoid letting it cross the permissible levels.
- A diet that’s low in sodium and proteins goes a long way in keeping your kidneys function well for longer.
- Increase intake of fresh foods, whole grains, healthy fats and lower intake of salty processed foods.
- This also helps in lowering weight and preventing obesity, which are important for preventing the onset of diabetes.
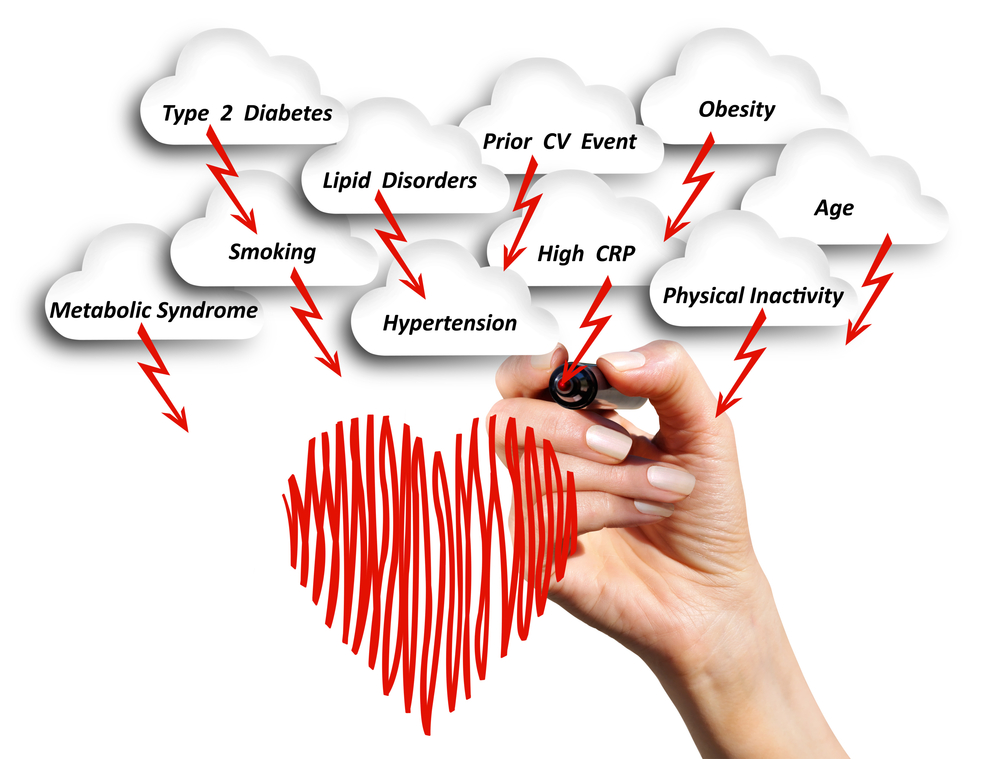

What are the Symptoms of Metabolic Syndrome?
The thing with Metabolic Syndrome symptoms and signs is the disorders associated with this are not obvious most of the time. However apart from the risk factors mentioned above, there are some common symptoms which experts have identified. These common symptoms have been listed below for your reference and knowledge:
- When an individual has a visibly large waist circumference and it is not reducing despite all efforts.
- A high blood sugar level which then results in other symptoms like an increase in fatigue, an increase in the number of times you urinate, an increase in thirst and developing a blurry vision.
Who is at Risk?
There are quite a few Metabolic Syndrome risk factors that all individuals should be aware about. We have mentioned them below for your reference and understanding of the same:
- An increase in age increases the chances of developing this
- The ethnicity of the individual also increases the risk. It is said that Hispanics and especially women are more prone to this
- Being obese or obesity increases chances
- A family history of type 2 diabetes or getting diabetes during pregnancy like gestational diabetes.
- Having other diseases like polycystic ovary syndrome, non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and sleep apnea.
What are the Causes of Metabolic Syndrome?
The Metabolic Syndrome causes identified by experts has been discussed below for your understanding.
- It is very closely linked to inactivity, obesity and being overweight
- Having insulin resistance also leads to this because the cells stop responding normally to insulin and glucose then cannot enter the cells so easily.
- Causes the blood sugar levels to rise even though the body churns out more and more insulin in an attempt to lower your blood sugar level.
How is Metabolic Syndrome Diagnosed?
For Metabolic Syndrome diagnosis, a metabolic syndrome doctor will need to perform a certain number of Metabolic Syndrome tests that will help to detect three or more signs of this disorder.
The doctor may check one or more of the following for better diagnosis:
- The circumference of your waist – more than 35 inches for women and 40 inches for men
- Your blood triglycerides while fasting
- An individual’s cholesterol levels
- Their blood pressure – 130/85 mm Hg or higher
- The glucose level while fasting – 100 mg/dL or higher
If there are abnormalities associated with three or more of these above-mentioned tests then that will help the doctor to confirm the presence of metabolic syndrome in the individual.
How is Metabolic Syndrome Treated?
Metabolic Syndrome treatment is treated through making lifestyle changes in the individual like the ones that have been mentioned below.
- Regular physical activity as part of your daily life
- Dietary changes
- Weight loss
- Managing and reducing stress levels
- Quitting smoking or reducing
How can Metabolic Syndrome be Prevented?
There are no set rules as such for Metabolic Syndrome prevention as it does not happen overnight, however there are some recommended lifestyle changes that an individual can make to ensure they do not develop of any of the 5 risk factors associated with this.
Some of these have been mentioned below for your understanding and consideration:
- Maintain a healthy waist circumference
- A healthy blood pressure
- A healthy cholesterol levels
- Regular exercise and weight loss
- A diet that is rich in fruits, vegetables, proteins, fibre, vitamins and the good fats
- Maintaining a healthy weight
Acute Pancreatitis
What is Acute Pancreatitis?
The pancreas is an organ that secretes hormones like insulin and several digestive enzymes. It is situated right behind the stomach. The inflammation of the pancreas is called acute pancreatitis.
What are the Types of Acute Pancreatitis?
- Mild acute pancreatitis: In this condition, the inflammation in the pancreas is mild.
- Severe acute pancreatitis: When the inflammation in pancreas is very severe, it is known severe acute pancreatitis. This can trigger fatal complications if not treated well.
What are the Symptoms of Acute Pancreatitis?
Acute pancreatitis is marked by a sharp pain in the upper abdominal region which ultimately reaches up to back. Other Symptoms include-
- Sudden pain in the upper abdomen
- Rarely, pain also starts in the lower abdomen
- If not controlled, pain starts moving towards the back
- Nausea and vomiting
- Rapid pulse
- Loss of appetite
- Diarrhoea
- Mild fever
- Pain while taking deep breaths or doing vigorous movements
- Fluctuations in blood pressure which eventually may cause faintness
Who is at Risk?
Some of the Risk Factors for developing Acute Pancreatitis are-
- Drink too much alcohol
- Smoke tobacco
- Have a family history of tumours or any other pancreatic condition
- Have diagnosed with having gallstones
There are certain conditions that can lead to developing Acute Pancreatitis.
- Cystic fibrosis
- Kawasaki disease
- Infections like mumps and mycoplasma
- Reye’s syndrome
What are the Causes of Acute Pancreatitis?
Acute pancreatitis can occur directly and indirectly. While direct causes affect the pancreas itself, the indirect causes are conditions or diseases that originate somewhere else in the body. Some common reasons for acute pancreatitis usually are as follows:
- Alcohol: Consuming alcohol regularly for many years can cause inflammation in the pancreas.
- Gallstones: Small stones like structures in the gallbladder can cause blockage in the enzyme secretion duct. The effect of this blockage eventually reaches up to the pancreas and starts causing inflammation.
- Infections: Several kinds of bacterial and viral infections in the blood can develop acute pancreatitis.
Some other not so common causes include
- Injury in the pancreas
- Abnormal levels of calcium in the blood
- Excessive triglyceride in the blood
- Genetic Mutations
How is Acute Pancreatitis Diagnosed?
Acute pancreatitis is diagnosed done by analysing the symptoms and examining the abdomen. If the doctor finds your symptoms similar to that of acute pancreatitis, and your abdomen shows sensitivity to touch, there are high chances that you have developed acute pancreatitis.
However, if the doctor is unsure by physical examination, some acute pancreatitis test might be taken. A few common tests are:
- Blood test: To check the amount of two digestive enzymes called amylase and lipase, doctors take the blood test. High amount of these enzymes indicates acute pancreatitis.
- ERCP scan: In this test, a thin tube with a camera is inserted into the digestive system to detect gallstones.
- Ultrasound: An ultrasound scan is usually done to have an image of the pancreas and gallbladder.
How is Acute Pancreatitis Treated?
Unlike other common diseases, Acute Pancreatitis cure needs extra care. If someone is diagnosed with the conditions, the following steps are done to treat the condition:
- Treatment starts with the hospitalization
- You may be admitted to take tests and given intravenous fluid.
- Medicines are given to lower the chances of any infection and reduce pain.
- If medications don’t work, surgery might be done to remove the damaged part of the organ or remove gallstones.
How can Acute Pancreatitis be Prevented?
By following healthy eating and drinking habits. Some of the prevention measures you can take to keep a check on acute pancreatitis are -
- Drinking water regularly can reduce the chances of having pancreas infection.
- Take alcohol in a limited amount. If you are diagnosed with acute pancreatitis, you should stop taking alcohol altogether.
- Eat a low-fat diet.
- Perform regular exercise and lose excess weight
- Quit smoking
Postprandial Blood Glucose Levels
Measuring Blood Glucose Levels is an essential step in managing diabetes. One such important tool used for glycaemic control is Postprandial Blood Sugar (PPBS). Postprandial or Post-Meal Blood Glucose Levels refers to the blood sugar levels after having a meal. Currently, Diabetes screening uses the fasting metabolic state to determine the risk of metabolic health. But recent studies have stated that one criteria for a test to be considered as an acceptable and reliable way to predict metabolic health, is that the test should be able to detect the preclinical stage of condition which is often missed when checking fasting blood sugars.
This is where post-Meal blood sugar becomes an important factor in assessing the body's ability to respond to sugar spikes, thus providing you with a better picture of your metabolic health. Let's see and learn why post-meal sugar levels are critical in the management of Diabetes.
Do Postprandial Blood Glucose levels matter?
Postprandial Blood Sugar (PPBS) is primarily used to diagnose Diabetes, detect complications of diabetes and to track the results of diabetes treatment. Studies show that postprandial sugar levels are a better marker than fasting glucose levels, independent of meal intake. Your pancreas secretes a hormone called Insulin which helps to regulate blood sugar levels in the body. Postprandial sugar levels provide you a clear glimpse of your insulin sensitivity and how efficiently this hormone is working to uptake glucose from the blood and into your cells after a meal.
Normally, it takes about 10 minutes post meal for the carbohydrates present in the meal to cause a rise in your blood glucose levels. This rise in sugar levels triggers your pancreas to secrete insulin which brings the sugar levels in the bloodstream. back to normal in 3-4 hours.
In Prediabetes and Type 2 diabetes, the mechanism of controlling sugar levels is impaired due to either the pancreas not secreting insulin or secreting a very small quantity of insulin which is not effective enough to control sugar levels. This leads to a state of continuously raised postprandial sugar levels which over time leads to insulin resistance. Research shows that elevated 1-hour level proves significant even if the 2-hour levels were within normal glucose tolerance range.
What is the Test is used to measure Postprandial Blood Sugar Levels?
There are two common methods used to perform the postprandial glucose blood sugar test.
1. Post-Meal Blood Sugar Check
Eat a normal meal lasting no longer than 20 minutes and then check your PPBS exactly 2 hours after the start of the meal.
2. Oral Glucose Tolerance Test (OGTT)
After fasting overnight, drink the high sugar beverage (usually 75g Glucose) given by your doctor, finish it within 20 minutes and then check your PPBS exactly 2 hours after the drink was started. Diabetes is diagnosed at 2-hours blood sugar of greater than or equal to 200 mg/dl
What are the ideal values for Postprandial Blood Sugar Levels?
American Diabetes Association (ADA) Recommended PPBS Target Levels
|
Timing |
Post 1 Hour |
Post 2 Hours |
|
Target PPBS (Normal) |
Less than 160 mg/dl |
Less than 140 mg/dl |
|
Target PPBS (Diabetes) |
Less than 180 mg/dL |
Less than 160 mg/dL |
A 1-Hour PPBS below 180 mg/dL indicates that your Beta cells are still preserved and can be brought back to a healthy state.
Why is it problematic to have continuously elevated Postprandial Blood Sugars?
Elevated levels of sugar even after 4 hours may indicate that insulin is not working to uptake the sugar back into the cells. Too much sugar in the blood is not desirable, and if this condition persists, the person becomes susceptible to Diabetes. This compromises glucose metabolism and has a huge impact on other parts of the body. It gives rise to a wide array of complications causing weakening of the nerves, kidney dysfunction, and eye damage.
Too much blood sugar induces oxidative stress in the body, leading to the production of free radicals. These free radicals damage the body cells, creating the imbalance capacity of the body to counter this effect via antioxidants. Increased levels of oxidative stress damage the blood vessels, leading to cardiovascular complications, like atherosclerosis and heart damage. Recent studies have pointed out that postprandial blood sugar level is also an important indicator of heart-related issues in comparison with fasting blood sugar.
Are High Postprandial Blood Sugar an issue for non-Diabetics?
Glucose levels in the blood elevate when food is introduced into the body. The pancreas then releases insulin into the bloodstream. Insulin assists the body in transferring glucose from the bloodstream into tissue and fat cells, where it can be stored for energy. When the system is working, blood glucose levels should be back to normal within 2 hours of eating.
In people with diabetes, however, the pancreas may not produce the proper amount of insulin, or there may be insulin-blocking cells that stop the insulin from transferring the glucose. In this case the glucose level would still be elevated 2 hours after eating. Increased levels of blood sugar or hyperglycaemia, even if you are not diabetic, can increase your chance of contracting this condition in the future.
Bottom Line
Diabetes can usually be managed with insulin, medication, diet, exercise, and lifestyle changes. Early detection and continued vigilance in monitoring of blood glucose levels is imperative when treating diabetes. If diabetes is left untreated, the elevated levels of insulin in the blood can result in a number of serious health problems, including heart disease, organ failure, foot ulcers, and blindness.
Postprandial glucose levels are soon becoming the ideal way to assess the functioning of your beta cells. The 1-hour measurement is more sensitive than the 2-hour value for identifying high-risk individuals, predict risk of diabetes complications, mortality, and hence may end up replacing the traditional 2-hour test in clinical practice.
PPBS is required to manage diabetes and identify impaired blood glucose levels. The levels are also influenced by diet types, frequency and sleep cycles, making it all the more critical to get yourself screened even if you're not diabetic. In fact, even apparently healthy individuals should test for diabetes, and those who are at higher risk like obesity should be tested more frequently.
The Side Effects of taking Insulin
Why do we need Insulin?
A healthy human body produces insulin to regulate the transportation of glucose from the blood into the cells. However, in diabetes, insulin may not be available for the effective movement of blood glucose into the cells. It leads to elevation of blood glucose levels and subsequent complications. Prolonged elevation of blood glucose can lead to several complications as follows:
- Kidney damage
- Nerve conditions
- Blindness
- Non-healing wounds leading to loss of limbs
- Sexual problems
- Strokes
- Heart attacks
In type 1 diabetes, the pancreas loses the ability to produce adequate insulin. The individual needs insulin supplementation for life to ensure glucose uptake from the blood. The onset of type 2 diabetes is usually in middle age.
In this condition, the pancreas does not produce enough insulin, or the available insulin is not helpful. In addition to these lifelong conditions, insulin therapy is also effective in gestational diabetes, insulin resistance, and diabetic ketoacidosis.
Insulin Side Effects
Before we dive deeper into the side effect profile of insulin, let us know the common side effects of using insulin as a long-term treatment option in type 1 and type 2 diabetes:
- Hypoglycaemia: Present in over 40% of individuals using insulin
- Weight Gain: Seen in approximately 33% of insulin users
- Headache: may be present in up to 33% of insulin users
- Flu-like Symptoms: These may be experienced by up to 13% of patients using insulin
One can appreciate from the above data that hypoglycaemia is the commonest insulin side effect that may cause severe complications. Let us discover the side effects of insulin by considering different parameters.
1. General Side effects of Insulin
Insulin use may lead to weight gain and increase in body fat. Sudden restoration of glucose control in individuals who did not have normal glucose levels in the past may cause swelling after initiation of insulin therapy. More efficient utilization of calories because of insulin therapy can also result in weight gain.
1. Heart-related Side Effects
Insulin may cause accentuation of cardiac side effects such as narrowing and hardening of cardiac arteries with the build-up of plaque (atherosclerosis). Moreover, insulin may contribute to hypertension by supporting other risk factors.
2. Endocrine Side Effects
The endocrine-related side effect of insulin is hypoglycaemia, as mentioned earlier. It is more common in patients with type 2 diabetes who are more prone to experience hypoglycaemia following insulin therapy. Hypoglycaemia causes sweating and confusion and is easily recognizable. Reversal of hypoglycaemia is possible by consuming sweets. However, there can be fatal complications if the individual cannot recognize the symptoms of hypoglycaemia. There is also a possibility of some renal (kidney) side effects because of insulin-induced hypoglycaemia.
3. Dermatologic Side Effects of insulin
Because insulin has a role in the formation of fat, one may experience collection of fat in some areas as a side effect of insulin. Frequently changing the insulin injection site or using a purer form of insulin may reduce the incidence of this side effect.
FAQs
1. What are the long-term side effects of Insulin?
Long-term use of insulin therapy to achieve blood glucose control in type 2 diabetes patients may increase the risk of cardiovascular disorders and some cancers. These side effects are more likely in patients with a history of heart problems.
2. Is Insulin harmful to the body?
Insulin has a remarkable potential to lower blood glucose with no severe side effects in most individuals. However, excess insulin in the blood or hyperinsulinemia may elevate the risk of obesity and cardiac side effects.
3. Why is taking Insulin bad?
Insulin drives glucose in the blood into cells. As the cells absorb more glucose, there is a possibility of hypoglycaemia if insulin administration is at the wrong time. Failure to consume food after insulin injection causes a severe drop in blood glucose levels. Insulin also causes an increase in the risk of heart conditions, stroke, and eye complications.
4. Does Insulin impact your kidneys?
Consistently high blood glucose levels lead to kidney damage in diabetes. Insulin therapy helps achieve predictable control of blood glucose levels and may prevent the development of kidney disorders.
Hyperthyroidism
What is Hyperthyroidism?
Hyperthyroidism is essentially a condition of the thyroids. The thyroid, which is a small gland shaped like a butterfly is located at the front of your neck. It produces two primary hormones known as tetraiodothyronine (T4) and triiodothyronine (T3) which control how your cells utilize energy. When an individual has hyperthyroidism then it means that the thyroid is producing too much of either T3 or T4 or both.
The three common types of Hyperthyroidism that experts essentially know of:
- Diffuse toxic goiter
- Toxic multinodular goiter
- Toxic adenoma
Hyperthyroidism Symptoms
There are quite a few Hyperthyroidism symptoms that individuals must know about. There are some that require immediate medical attention and some that do not and can be treated otherwise.
We have listed some of the most common ones across the different types and depending on their intensity, before for your reference and knowledge:
- Elevated blood pressure
- Rapid heart rate
- Hand tremors
- Excessive sweating
- Developing a low tolerance for heat
- More frequent bowel movements
- Rapid weight loss
- Irregular menstrual cycle
- An increase in appetite
- Restlessness
- Nervousness
- Difficulty in sleeping
- Increase in hair loss
- Vomiting and nausea
- Development of breasts in men
- Shortness of breath
- Dizziness
- Loss of consciousness
These are some common reasons for Hyperthyroidism that people experience.
Who is at Risk?
There are various Hyperthyroidism risk factors as it can happen to anyone due to multiple reasons. However, experts have been able to identify certain possible risk factors related to this. We have mentioned them below for your reference and understanding of the same:
- Someone who is suffering from certain medical conditions like viral infections and autoimmune disorders
- Pregnant women
- Even though this can happen to anyone irrespective of age but is known to be more common in people who are above the age of 60.
- Women are more likely to develop this than men
- Genetic factors
Hyperthyroidism Causes
There are a variety of Hyperthyroidism causes which have been identified by health experts. Graves’ disease which is an autoimmune disorder is known to be the most common cause of this condition. Apart from that, we have discussed below for your understanding some of these causes in details:
- An increase in iodine which is said to be the key ingredient in T3 and T4.
- Testes or tumours of the ovaries
- Benign tumour of the pituitary gland or thyroid
- When an individual has consumed large amounts of tetraiodothyronine through either medications or dietary supplements
- Thyroiditis or inflammation of thyroid
How is Hyperthyroidism diagnosed?
For Hyperthyroidism diagnosis, a Hyperthyroidism doctor will need to perform a certain number of Hyperthyroidism tests to understand if there are any underlying conditions that is causing Hyperthyroidism to happen in the first place. He will first conduct a physical exam and a get an idea of your complete medical history. The doctor may then have to conduct multiple tests to get to the root cause of the problem. Some of these tests include:
- A cholesterol test to check for cholesterol levels in the body. Low levels will be an indicator of an elevated metabolic rate
- Free T4, T4 and T3 tests to measure the amount of thyroid hormone present in your blood
- A thyroid scan
How is Hyperthyroidism treated?
There are different methods for Hyperthyroidism treatment. We have mentioned it below for you:
- A Surgery may be done to remove a section of your thyroid gland. Most people respond well.
- Radioactive iodine is performed on individuals to destroy the cells which are responsible for the production of the hormones.
- In certain cases, the doctor may prescribe some medicine for hyperthyroidism.
Health care provider offering a variety of services for various health conditions. They some of the best paediatricians from all over India to attend to any and all medical requirements. Their services are listed on their app and website. You should consider them if you’ve been wondering how to cure hyperthyroidism permanently.
How can Hyperthyroidism be prevented?
If you have been thinking about how to prevent Hyperthyroidism then it can be done by keeping some simple measures in mind. Some of these have been mentioned below for your understanding and consideration:
- Eating a good and healthy diet with an increased focus on calcium and sodium intake as these are essential minerals to keep hyperthyroidism at bay.
- Work with your doctor to chart out a good workout plan
- Include nutritional supplements in your daily life
- Take Vitamin D and calcium supplements to increase the health of your bones and make them strong again.
Hyperglycaemia
What Is Hyperglycaemia?
Hyperglycaemia is also known as high blood glucose and happens when the blood contains too much sugar. This condition is a sign of diabetes. The reason for having too much blood sugar is that the body does not have enough insulin or is unable to process the insulin properly. If this condition of having high blood sugar continues for a long time, then it can lead to damage to the nerves, blood vessels, and organs. Hence it is important to get proper treatment when you see symptoms of high blood sugar to prevent the effects of hyperglycaemia.
Hyperglycaemia Symptoms
Hyperglycaemia symptoms do not appear until the glucose levels get too elevated. The signs and symptoms of hyperglycaemia occur when the glucose levels are above 180 to 200 mg/DL. The symptoms last as long as the sugar levels remain high and the condition worsens.
Early symptoms are:
- Feeling thirsty despite drinking enough water
- Frequent urination
- Headache and fatigue
- Blurry vision
- Wounds that do not heal
If the blood sugar levels are not controlled it can lead to a build-up of ketones in urine and blood. These ketones are toxic acids and are called ketoacidosis. It includes:
- Breath smells fruity
- Abdominal pain
- Dry mouth
- Confusion
- Nausea and vomiting
- Shortness of breath
- Weakness
If you have the above symptoms then it is best to get tested for diabetes. People who have diabetes should often monitor the glucose levels so that there are no side effects of hyperglycaemia.
Who is at Risk?
The risk of developing hyperglycaemia is high in:
- People having a family history of type 2 diabetes
- People having high cholesterol and blood pressure levels
- Overweight and obese people
- Women with a family history of gestational diabetes
- Women who had gestational diabetes
- Women suffering from the polycystic ovarian syndrome, PCOS
- African Americans Hispanic, Asian Americans, and Native Americans are more at risk of high blood sugar than other groups of people.
- People who do not follow a healthy diet
- People who consume fried, processed, and sugary food
Hyperglycaemia Causes
The blood sugar levels can rise if the insulin is not produced properly or is not enough. The other causes of hyperglycaemia are:
- The amount of carbohydrates in the food is more compared to the insulin produced in the body.
- Physical stress or stress due to cold, flu, or other infections can affect blood sugar levels.
- Emotional stress due to work or family issues
- Hormonal issues can also result in hyperglycaemia
- Conditions like Cushing Syndrome can lead to insulin resistance
- Cystic fibrosis, pancreatic cancer, and pancreatitis can cause an imbalance in sugar levels
- Medications like diuretics and steroids can lead to hyperglycaemia.
- Pregnancy can lead to reduced insulin sensitivity.
- If the insulin dose that you are taking is not enough for our body.
How is Hyperglycaemia Diagnosed?
If you have even subtle signs of hyperglycaemia, it is best to get a hyperglycaemia diagnosis done by getting the blood sugar levels checked.
- A haemoglobin A1C test is a common hyperglycaemia test that is recommended by a doctor if there are signs of it. This test gives a 3-month average of the blood sugar level. It checks the percentage of blood sugar in RBC to the haemoglobin. If it is high then a treatment plan will be worked out by the doctor. This percentage is different based on age and certain other conditions like pregnancy. Older adults will have a higher range than others.
- Fasting blood sugar test is done by taking a blood sample after not eating or drinking anything for a minimum of 8 hours.
- Postprandial or after meal hyperglycaemia test is done to check levels after a meal.
- Urine test is done to check the presence of ketones and also glucose in the urine.
How is Hyperglycaemia Treated?
Hyperglycaemia treatment is a lifelong process and a person having it should take steps to ensure that there are no spikes in blood glucose levels. The treatment plan will include:
- Hyperglycaemia medicine to bring blood sugar levels to normal. Insulin injections may be recommended depending on the cause, age and severity. Altering of the medications may be done depending on the response to the medication and the side effects.
- The doctor will also recommend physical activity to reduce excess glucose in the blood. But if they find ketones in the blood, they should avoid exercise.
- A diet plan will be introduced where the diet will be moderated and low sugar foods will be included.
Hyperglycaemia care includes many things like medication, diet and exercise. The treatment should also be holistic along with regular monitoring.
How can Hyperglycaemia be Prevented?
Hyperglycaemia prevention tips are:
- Maintaining a physically active lifestyle which includes exercise to keep the blood sugar levels low.
- Follow a regular meal routine including a healthy hyperglycaemia diet which is rich in whole foods, fruits and vegetables.
- Maintain a normal weight
- Limit alcohol
- Avoid sugary, fried and fast food
- Avoid smoking
- Get regular health checks
Hypoglycaemia
What is Hypoglycaemia?
Hypoglycaemia is a condition where the blood sugar levels (glucose) is lower than normal. Often related to people with diabetes, Hypoglycaemia occurs when the body is deprived of insulin hormone that converts glucose into energy.
Blood sugar levels are considered low when they drop below 70mg/dL. A severe reduction in blood sugar levels can be dangerous.
Hypoglycaemia Symptoms
Hypoglycaemia symptoms can occur suddenly or gradually, depending upon the individual health conditions, lifestyle, etc. Some of the common symptoms across different people have been listed below for your understanding:
- Dizziness
- Restlessness
- Sweating
- Shakiness
- Rapid heartbeat
- Sudden nervousness and mood changes
- Sudden/unexplained fatigue and tiredness
- Hunger
- Confusion and difficulty in thinking clearly
- Tingling sensation in the skin and nerves
- Difficulty in sleeping
- Skin turning pale
People who are unaware of their Hypoglycaemic condition often fail to notice the symptoms and can faint due to a severe drop in blood sugar levels leading to experiencing a seizure or even going to coma.
Who is at Risk?
Hypoglycaemia risk factors differ from individual to individual depending upon the type of diabetes, age, health conditions, etc. Certain red flags for when an individual might be at risk are:
- Diabetic people are more prone to Hypoglycaemia than others
- Excessive dieting can lead to a drop in sugar levels
- Excessive smoking or drinking alcohol
- Too much insulin in the body can lead to Hypoglycaemia
- Too many medications, diabetic or other, can lead to Hypoglycaemia
Hypoglycaemia Causes
Hypoglycaemia causes can differ depending upon the triggers that have been making changes in the hormone levels. However, we have discussed some possible causes for you down below:
- Blood Sugar Regulation – Food contains carbohydrates and the body breaks down the carbohydrates (glucose) into energy with the help of insulin – a hormone secreted by your pancreas. Mismanagement of food habits or body functioning can result in an imbalance in the secretion of insulin levels, and cause sudden Hypoglycaemic episodes.
- Insulin intake for Diabetics – People with diabetes manage their insulin levels with medicine (Type 2 diabetes) or insulin shots (Type 1 diabetes). Any imbalance in insulin intake can cause hypo or hyperglycaemia.
- Excessive alcohol consumption – drinking too much alcohol can block your liver and stop it from releasing the stored glucose into the bloodstream – inflicting Hypoglycaemia
- Serious health conditions – Critical diseases like cancer, tumour, endocrine problems, insulinoma, etc sometimes induce episodes of Hypoglycaemic
How is Hypoglycaemia diagnosed?
If one experiences symptoms of Hypoglycaemic, it is always best to get a Hypoglycaemic diagnosis immediately by checking blood sugar levels. If you don’t have the glucometer with you, a visit to the doctor is very much important.
- Physical Examination – When the doctor determines symptoms of Hypoglycaemia, they take a Hypoglycaemia test immediately and monitor the sugar levels constantly for preventing from fatal episodes
- Studying history – Doctor examines your dietary habits, lifestyle habits, medical history, etc to know the probable cause of diabetes
- Monitoring glucose levels – Doctor may recommend carrying a glucometer or glucose-sensor to study intervals of low blood sugar levels and understand the pattern.
How is Hypoglycaemia treated?
Hypoglycaemia treatment is done on the understanding if one is diabetic or not. It starts with controlling the ongoing drop in the blood sugar levels by consuming at least 15 grams of carbohydrates immediately.
- Controlling Hypoglycaemia: Eating 15 grams of quick-digestible carbohydrates i.e., fruit juice, dried fruit, cookies, pretzels, toffee, etc to control the ongoing Hypoglycaemia
- Dietary changes: Consuming food at regular intervals is one of the distinct measures to balance blood sugar levels. Make sure you eat a nutritive diet with the right balance of carbohydrates, protein, and fats.
- Medication – For diabetic patients, doctors recommend Hypoglycaemia medicine in the form of tablets and insulin shots to maintain insulin levels for optimum production of glucose in the body.
How can Hypoglycaemia be prevented?
Hypoglycaemia prevention can be done in several ways. These include:
- Regular checking of Blood Sugar Levels – If you have had Hypoglycaemia in the past, then checking blood sugar levels on intervals helps in saving from further occurrence
- Snack Smart – Consider eating a 6-meal diet and snacking at the right time to ensure your blood sugar levels never drop below the normal
- Exercise right – indulge into the right kind of exercises and keep yourself fuelled with energy bars, sports drinks, etc to save from Hypoglycaemia during exercises
- Draft your lifestyle – Maintain a balanced and healthy lifestyle with proper meal ad sleep patterns to save from any Hypoglycaemia episodes.
Vanquishing Visceral Fat
The one place on our body that we all dread putting on weight is the abdomen. Unfortunately for us, it ends up being one of the areas in our body that is most prone to store or accumulate fat quickly but very hard to burn off. An additional cause for concern is that this abdominal obesity is not something that is seen due to an underlying illness or condition. A majority of the time we have ourselves and our unhealthy diet and sedentary lifestyle to blame for it.
When it comes to Type 2 Diabetes, Abdominal fat becomes very active and secretes a group of hormones called adipokines that impair glucose tolerance. Abdominal obesity also raises serum resistin levels, which in turn directly correlates to insulin resistance. Researchers have found that waistline adipose tissue is the foremost type of fat deposits that contribute to rising levels of serum resistin. Fortunately, research also shows by losing that very abdominal fat, serum resistin levels also decrease rapidly.
What is Abdominal Obesity and why is it a matter of concern?
Abdominal obesity, also known as central obesity and truncal obesity, is when excessive abdominal fat around the stomach and abdomen has built up to the extent that it is likely to have a negative impact on health. Abdominal Fat is often called by many names like Belly Fat, Beer Belly, Paunch, Pot Belly etc. and is of Two Types: Subcutaneous and Visceral Fat. Compared to Subcutaneous Fat that lies just underneath your skin, Visceral Fat is a bigger concern since it is a known high-risk factor for a variety of health issues.
Resistin is a protein found to be produced and released from adipose tissue to serve endocrine functions in our body. Studies show that Visceral fat contains and increases the amount of 'Resistin' in the blood. High Serum Resistin levels not only cause inflammation of the body’s tissues and organs but also narrows your blood vessels, resulting in several comorbid issues. Visceral Fat has been strongly linked to some serious medical conditions like Stroke, Type 2 Diabetes, Heart Disease, High Cholesterol and even Alzheimer's. In Type 2 diabetes, insulin resistance causes your body's muscle and liver cells to stop adequately responding to normal levels of insulin. This leads to Glucose levels rising in the blood heightening the risk for diabetes.
What is Visceral Fat?
Visceral fat is abdominal or belly fat that lies out of reach and deep within the abdominal cavity covering the spaces between our internal organs. It is the "active fat" surrounding abdominal organs and affecting the body's hormonal functions and associated with metabolic and chronic inflammatory diseases, giving it the moniker "dangerous fat tissue."
What are the ill effects of having Visceral Fat?
- Triggers chemicals and hormones that increase inflammation.
- Triggers the release of excess fatty acid into the blood impairing kidney function.
- Decreases insulin sensitivity.
- Increases bad cholesterol also called Low-Density Lipoprotein (LDL) levels.
- Elevates blood pressure.
What is the Difference between Subcutaneous & Visceral Fat?
1. Subcutaneous Fat
Located between the skin and the outer abdominal wall. It is the jiggly, pinchable fat located just underneath the skin.
2. Visceral Fat
Stored inside the abdominal cavity and lies in the spaces between the abdominal organs, which is firm, hard and what is most popularly called a “Beer Belly”
Why is Visceral Fat Harmful for Health?
Although both Subcutaneous and Visceral fats release hormones, the latter is more likely to interfere with organ functions given its proximity to the surrounding vital organs of the abdominal cavity such as the liver, intestine, and pancreas.
An increased amount of Visceral Fat, results in an increased risk of developing chronic conditions like
- Insulin resistance and Type 2 Diabetes
- High Blood Pressure
- Hyperlipidaemia
- Risk of Stroke and other Heart Conditions
-
How can we prevent Visceral Fat from accumulating?
1. Exercise
Exercise is the most effective way to shed off abdominal fat. The two most favourable types of exercises are - Cardiovascular and Strength Training Exercises. This not only increases cardiac output, but also helps keep the body toned and in shape.
- Cardio Exercises: Cycling, Aerobics, Swimming, Running
- Strength Exercises: Push-ups, Weight lifting, Squats
-
2. Stress
Excess abdominal fat accumulation is also a result of stress. When a person is nervous, their body releases a hormone called cortisol, which causes their body to store more visceral fat. According to some doctors, people with elevated visceral fat levels can aim to reduce their stress levels. Meditation, deep breathing practice, and other stress-reduction exercises may be helpful and support abdominal fat loss.
3. Diet
A healthy diet includes a lower intake of salt, sugar, and refined foods, which will aid in weight loss and the removal of excess abdominal fat. Some ways to do that is -
- Pay attention to portion size
- Emphasize complex carbohydrates (fruits, vegetables, and whole grains)
- Avoid simple carbohydrates such as rice and sugary drinks.
- Choose Fresh and seasonal fruits and vegetables.
- Choose Lean proteins like Beans, Peas and Lentils.
- Choose to cook your foods by Boiling, steaming, grilling, and baking instead of frying.
- Choose Soluble fibres like nuts, seeds, barley, sprouts, avocados, and oats.
-
How is Visceral Fat Diagnosed?
What do people make that you can’t see?
The right answer is Noise! But an equally acceptable answer would have been Visceral Fat!
While body fat that accumulates in the belly area may serve as an tell-tale indicator of visceral fat, you can’t see visceral fat with the naked eye. Visceral fat hides beneath the surface, surrounding your internal organs. Then how can we diagnose or measure Visceral Fat? There are multiple ways to measure visceral fat, but not all of them are practical or accurate.
1. CT SCAN / DEXA / MRI*
Although these modalities are the most reliable process to measure the Volume of Visceral Fat, they are not the most practical. They are cumbersome, time consuming, need specialized machinery, expensive or not cost-effective, and would subject one to unnecessary exposure to radiation. *Computed Tomography, Dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry, Magnetic Resonance Imaging
2. BMI
Body mass index (BMI) has long been considered a helpful recommendation for self-assessing our weight. BMI involves weighing yourself (in kilograms) and dividing the result by our height (in meters squared). For Indians, a BMI of 23 or higher is considered can be indicative or a sign of visceral fat.
3. Waist Circumference
This is an easy way to estimate the presence and volume of visceral fat. To measure your waist circumference, take a tape measure and wrap it around your waist over your belly button, without sucking in your stomach. The normal waist measurement for women is up to 35 inches (80 cms) and around 37 inches (94 cms) for men. Anything higher indicates the presence of visceral fat.
4. Waist - to - Hip Ratio (WHR)
Unlike Body Mass Index (BMI) which is obtained by calculating the ratio of your weight to your height, Waist to Hip Ratio measures the ratio of your Waist Circumference to your Hip Circumference. It is an easy, inexpensive, and accurate way to determine the amount and proportion of stored fat on the waist, hips, and buttocks. The ideal WHR according to the WHO should be 0.9 or Lesser (for Men) and 0.85 or Lesser (for Women).
Several research studies have shown that WHR is an effective predictor of health risks, especially cardiovascular disease and diabetes. Some of the benefits of WHR in determining Health Risks even when the BMI is normal or moderate are-
- A High WHR is linked to an increased risk of early death
- Accurate tool for predicting Hypertension.
- Decreasing WHR even by just 5%, significantly lowers the risk of chronic kidney disease and Non-alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease.
- Useful as a gauge of obesity in older adults whose body compositions have changed.
-
What Causes Visceral Fat to accumulate?
There are multiple factors that could be contributing to the body organs storing visceral fat.
1. Excessive Energy Intake
This is the most crucial cause for fat storage. When we consume carbohydrate-rich food, we are force-feeding or overloading our body with glucose or energy. This excessive energy has no choice but to transform itself into fat and get stored in our tissues. Although this fat can be present in both subcutaneous and visceral tissues, over time the adipose cells lose their ability to retain this extra fat, and have no choice but to start accumulating as visceral depots in places surrounding internal organs where it normally doesn't, thus not being accessible even to be recycled.
2. Stress
Plays a key role in our bodies storing visceral fat. The Stress Hormone - Cortisol is known to significantly increase the retention of visceral fat.
3. Genetics
Unfortunately, some of us may just be genetically predisposed to depositing weight around our middles due to our body shape or just the way that our bodies work. For example, “Apple Shapes” tend to retain weight around their middles, while “Pear Shapes” carry weight lower.
How do we get Rid of Visceral Fat?
Start and Maintain a Healthy Lifestyle, both Physical and Mental! That's it - plain and simple.
1. Diet
- Increase intake of plant-based foods from making fruits and vegetables at least 70% of your daily diet.
- Reduce or Avoid Trans fats which are commonly used in the creation of various substitutes of natural oils mostly found in all processed foods.
- Eliminate foods with a high glycaemic index, as they can dramatically increase the sugar content in your blood, which increases insulin synthesis, resulting in formation and storage of excess fat on your waistline.
- Minimize and Avoid consumption of alcoholic beverages and salty snacks accompanying it.
- Eat foods that are high in fiber
- Consume Nuts, dried fruits, citrus fruits, raw vegetables, and fruits as alternative to any other snacks.
-
2. Exercise
Exercising an excellent Antidote to Visceral Fat. It does not have to be any high intensity gym sessions. Just giving your body the chance to move will help you get started. Take long walks post meals, play your favourite sport, cricket, football, swimming or even just playing hopscotch with your kids-everything counts!
3. Stress
Prolonged stress can affect your mental and physical health. It can even lead to a little extra weight around the middle, and extra abdominal fat isn't good for you. There are studies that even suggest that Visceral Obesity is a Physiological Adaptation to Stress! Meaning this is nothing short of a vicious cycle. Stress Management is a key factor in the management of reducing visceral fat.
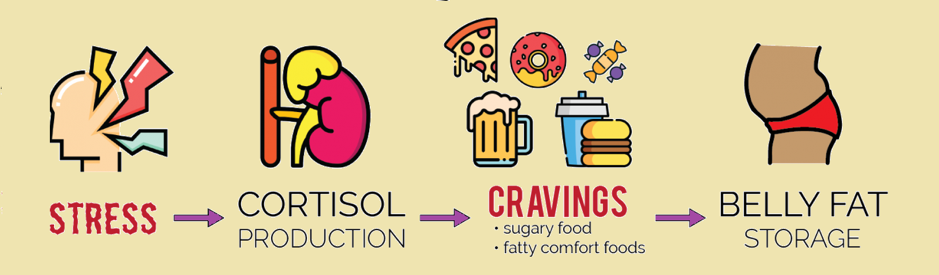
The Role of Stress in Belly Fat
4. Sleep
The quantity and quality of your sleep have a direct impact on your cortisol levels and weight. In other words: inadequate sleep is a stressor! Most people need 7-9 hours of uninterrupted sleep per night. In order to make this happen, make sure you have a consistent bedtime of around 10 pm. Turn off electronics 1-2 hours before bedtime, and do something relaxing like reading or taking a bath.
Bottom Line
Visceral fat is fat that we can't see, it's not easy to tell if someone has too much of it. The health threats associated with high visceral fat levels are severe, making it essential for anyone who is overweight or suspecting high levels of visceral fat levels to get it checked out at the earliest. Visceral fat gathers around the organs and it gets there the same way as other fat – through poor diet, lack of exercise and genetics. In today's world where everything is instant and 24X7, there is new information thrown at us every week. But how many of us actually understand or assimilate that information and recognize if it may be applicable to us individually?
Since the symptoms or nature of visceral fat is that it cannot be seen, many of us don't give it a second thought and only start to do something about it when our health starts deteriorating enough for us to feel it. But remember, the more often and longer the blood insulin levels remain high, the more likely you are to accumulate excessive body fat and ending up battling weight problems. When it is so difficult to even know or understand if we are at risk of health diseases, it is even more confusing to trust what health recommendations are truly effective. The secret mantra for this is to just start living a healthy and balanced lifestyle. These 4 words are powerful enough to prevent and later burn off the multiple fat deposits you may be storing. So, start today, evaluate the fat you see around your midsection using any of the methods mentioned above - BMI, Waist Circumference and Waist - to - Hip Ratio, and gauge how you measure up!
Effects of Fasting on Metabolic Health
Can changes in dietary habits help in improving your metabolic health? Various studies conclude that fasting does help in enhancing overall wellbeing which also includes metabolic health. Fasting helps in maintaining your glycaemic levels, improving insulin sensitivity, reducing insulin resistance and thus enabling weight loss. But before we get into the workings of the overall metabolic functioning of your body, let’s start with the basics.
What is Fasting?
Fasting can be defined as a duration of voluntary abstinence or restraint from food and drink. Fasting can be done by either reducing the amount of food you eat, or by restricting the intake of calories in that particular duration. Fasting has been a practice throughout human evolution right from the time of hunter-gatherers. Just like we have evolved to be in sync with the circadian rhythm (day/night cycle), our metabolism also has adapted to daytime food and night time sleep.
There are a number of reasons for an individual to adopt a fasting regime - to lose weight, for religious/spiritual reasons or just as a lifestyle strategy to improve your health. Although, every person performs fasting in his or her own way, finding an eating pattern that suits you and your reasons for doing it may sometimes not be what's best for you. So, to decide on which approach might be the right fit for you, lets learn about the various types of fasting.
What are the Types of Fasting?
There are many types of dietary approaches that involve interspacing planned periods of fasting with regular eating. Some of the most popular and effective types of fasting are as elaborated in the table below.
|
Type |
Method |
Example |
|
Intermittent Fasting OR 16:8 Diet |
Fast for 14 to 16 hours a Day and limit your eating window to 8 to 10 hours. Based on your preference, you can consume two to three meals within this eating window. |
A 16-hour fasting window would be like if you eat your dinner at 8 pm on Monday and fast until your next meal at 12 pm noon on Tuesday. |
|
Periodic Fasting OR 5:2 Diet |
Restricting your calorie intake 500 - 600 kcals for 2 days in the week and eating normally the other 5 days. |
Eat small meals not more than 600 kcals on Tuesdays & Fridays. Continue eating regular meals on the other 5 days. |
|
Eat Stop Eat OR 24-Hour Fasting |
24-hour Fasts Once or Twice a Week. |
A 24-hour fasting window would be like if you eat your dinner (last meal) at 8 pm on Monday and fast until your next meal at 8 pm on Tuesday. |
|
Alternate-day Fasting |
Fast every other day by restricting quantity of either consumption or calories to less than 600 kcals. |
Eat your regular meal on Monday, restricted calorie intake to 500 kcals on Tuesday, and go back to eating a regular meal on Wednesday. |
|
Extended Fasting |
It is a form of intermittent fasting that involves an extended pause on eating, typically lasting for 2 days/48 hours or more. |
Eat your lunch at 2 pm (last meal) on Monday, and stop eating or start the fast from that same Monday evening until your next meal 48 hours later on Wednesday evening. While this fast involves eliminating foods that contain calories, it is still extremely important to drink plenty of noncaloric fluids, such as water, throughout the fast to keep the body hydrated. |
Remember, fasting affects people with underlying conditions differently. If you have Prediabetes or Type 2 Diabetes, talk to your care provider or coach before making dramatic changes to your diet. If you take insulin or are on blood sugar-lowering medications, it is even more critical to check with your doctor before engaging in any type of fasting, as it can plummet your blood-sugar to dangerously low levels and drastically alter how your medications work.
To learn more about Intermittent Fasting, Do's and Don'ts or how to pick the type of fast best suited to you, check out our article on Intermittent Fasting and Diabetes.
What are the Benefits of Fasting?
There are multiple benefits of Fasting. Some of them are:
- Weight Loss: Fasting may lead to weight loss due to two primary reasons. First, it restricts the intake of calorie, thus allowing the body to use its fat reserve. Second, it maintains a low level of insulin, thereby keeping the body in a fat-burning mode. It helps in shredding both your muscle and fat mass. Practicing it for a significant period may result in reducing the resting metabolic rate and assist in weight loss. When combined with resistance training, it decreases fat mass and improves health-related biomarkers. It also helps in reducing your appetite by maintaining Ghrelin levels which is a "hunger hormone" that tells you when to eat.
- Metabolic Flexibility: The body stores energy in the form of glycogen and fats. In high blood sugar levels, your cells use a part of this energy and stores the remaining portion in the liver or muscles in the form of fat or glycogen. During fasting, there is a depletion in glycogen reserve and the body switches to fat for energy. These facts are converted into fatty acids and then to ketones to produce energy. Using ketone bodies instead of blood glucose for energy may improve organ function, neural health, and overall muscle function. Switching between the fed and fasting state makes your body more metabolically flexible. During fed-state, the primary energy source would be glucose, while during the fasting state, your body uses fat as fuel. More the metabolic flexibility, more the fat burn after a heavy-fat meal.
- Insulin Sensitivity: A comprehensive research study assessing the long‐term effects of reduced intake on energy, states that calorie restriction reduces various cardiometabolic risk factors and significantly improves your insulin sensitivity index. Time-restricted eating helps in maintaining the circadian rhythm. Just changing the timing of meals, by eating earlier in the day and extending the overnight fast, significantly benefits metabolism. While a disruption in circadian rhythm may result in abnormal glucose metabolism and insulin resistance.
Managing Carbohydrate intake while Fasting
You should monitor your glucose intake to get the best out of fasting. Aim for a low glycaemic diet to improve metabolic flexibility. Some of the measures that may help you in strictly restricting your glucose uptake are:
- Breaking your Fast: Your hunger hormone called Ghrelin can make you crave for glucose or sugar, especially in the initial days of starting the diet. On eating, this can suddenly raise your sugar levels and cause even more food craving and irritability. So, it is essential to choose a meal that does not cause this surge in your blood glucose. Limit the hours of the day when you eat, and for best effect, make it earlier in the day (between 7 am to 3 pm, or even 10 am to 6 pm, but definitely not in the evening before bed and avoid snacking or eating at night-time.
- Monitor your Diet: Many people eat a heavy carbohydrate diet just before their fasting window. Avoid doing this as this takes more time for the body to switch to fat-based fuel. Avoid sugars and refined grains, and eat fruits, vegetables, beans, lentils, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats instead. Let your body burn fat between meals. Don’t snack and be active throughout your day.
Bottom Line
Eating healthy is simple, but it can be incredibly hard to maintain. At the end of the day, there is no one-size-fits-all solution when it comes to nutrition. If you feel good when fasting and find it to be a sustainable way of eating, it can be a very powerful tool to lose weight and improve your health. Along with fasting, exercising and taking care of your sleep are also important factors to focus on, so the best diet for you is the one you can stick to in the long run.
The effects of your Gut Microbiome on Metabolism
According to clinical conclusions gathered over the last two decades, the intestinal microbiota may lead to the human body's metabolic wellbeing and, when defective, to the pathogenesis of numerous common metabolic disorders such as obesity, type 2 diabetes, non-alcoholic liver disease, cardiometabolic disorders, and malnutrition.
Microorganisms, or microbes for short, are bacteria, viruses, fungi, and other microscopic living things—these bacteria in your intestines and on your skin. The intestinal microbiota is made up of most of the bacteria in your intestines, located in a "pouch" in the large intestine called the cecum.
Importance of Gut Microbiota
Did you know your Microbiome has a myriad of effects on your body as it ages? The gut microbiota is extremely important to your wellbeing because it aids digestion and benefits your immune system, among other things. Weight gain, elevated blood sugar, high cholesterol, and other conditions can be caused by an imbalance between harmful and healthy microbes throughout the intestines.
Here is how your Microbiome affects your health-
Digestion of Breast Milk: Lactobacilli, Bacteroides & Bifidobacteria are bacteria that first begin to develop within a baby's intestines as they are digesting breast milk. They break down the essential sugars for growth present in breast milk.
Fiber Digestion: Some bacteria break down fibre and produce short-chain fatty acids, beneficial to gut health. Fibre can help to prevent obesity, diabetes, heart disease, and cancer.
Controlling your Immune System: Your gut microbiome is also in control of how your immune system functions. The gut microbiome will influence how the body responds to infection by interacting with immune cells. A study published in Gut Microbes states that the gut microbiota, which lives in the gastrointestinal tract, benefits its host by controlling immune homeostasis, among other factors. Furthermore, it has recently been discovered that changes in gut microbial environments can contribute to immune dysregulation and autoimmune disorders.
Healthy Nervous System: In contrast to healthy individuals, people with multiple neurological conditions have distinct types of bacteria in their guts, according to several different research kinds. This means that the gut microbiota can affect brain wellbeing. Several studies have shown that some probiotics can assist with depression and other mental health problems.
Cardiac Health: According to new findings, our gut microbiota can play a role in some cardiac diseases. New research shows that maintaining a good stomach will help you have a healthier heart.
Effect of Diet on Gut Microbes
Surprisingly, the diversity of intestinal bacteria is determined by the food you consume. Getting so many harmful microbes, on the other hand, can cause disease. Gut dysbiosis refers to an imbalance between positive and harmful bacteria in the gut, leading to weight gain. Irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) and inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) are two intestinal diseases in which the microbiome can contribute to the symptoms. People with IBS can feel bloating, cramps, and abdominal pain as a result of gut dysbiosis. This is because microbes create many gas and other chemicals, which lead to intestinal pain symptoms.
Influence of Gut Microbiota on Diabetes
External interventions, such as diet, alter the gut microbiota, causing dysregulation and secretory modifications in intestinal microbial metabolites, activating various potential pathways contributing to insulin resistance and diabetes.
A research published on Acta Endocrinological (BUC) concluded that obesity and insulin resistance are closely linked to a chronic inflammatory condition. Any action aimed at preventing or treating type 1 diabetes mellitus in humans should prioritize the gut immune system. The only non-pharmacologic alternative for preventing type 2 diabetes mellitus will be constant microbial stimulation, well-controlled diets, and the use of probiotics and prebiotics. The new research focused on 33 babies who had a high genetic chance of having type 1 diabetes. It was found that the microbiome's richness fell significantly before the advent of type 1 diabetes. Also, the levels of some harmful bacterial organisms rose shortly before developing type 1 diabetes.
Probiotic for Healthy Gut Microbiota
Certain beneficial bacteria in the microbiota, on the other hand, may help to increase gut health. Probiotics and yogurt containing Bifidobacterium and Lactobacilli can help seal spaces between intestinal cells and avoid leaky gut syndrome. Also, taking Bifidobacterium and Lactobacilli-containing probiotics will help with IBS symptoms as they can also keep harmful bacteria from attaching to the intestinal wall, which can cause disease.
The risk of coronary heart failure, atherosclerosis, heart attack, and stroke is cut in half when cholesterol and hypertension are decreased. The good scientific evidence that probiotic intake reduces hypercholesterolemia and hypertension encourages these species to treat cardiovascular diseases.
Prebiotic and Probiotic Foods for Metabolic Health
Prebiotics are the precursors of probiotics. These compounds are made up of carbohydrates that humans can't digest (mostly fibre). This fibre is absorbed by the healthy bacteria (probiotics) in your stomach. On the other hand, probiotics are helpful microbes. There are living bacteria that can be present in several foods and supplements. They can be beneficial to one's wellbeing in several ways.
Bottom Line
The human gut is more complex than generally known, and it directly affects physical wellbeing. A high immune system, cardiovascular health, brain health, increased mood, good sleep, and successful digestion benefit a healthy stomach. It can also help avoid certain cancers and autoimmune disorders.
To keep yourself and your gut safe, emphasise an overall healthy lifestyle that requires lots of exercises, adequate sleep, and a diet high in natural foods, prebiotic fibre, and probiotic foods. Eat a wide range of fruits, nuts, whole grains, and fermented foods to promote beneficial microbes in your stomach.
12 Tips to Avoid Diabetes Complications
Do you remember how you felt when you were first diagnosed with diabetes? It was like something hit you out of the blue! But in time, you learnt more about your condition, what causes it, what makes it worse, and most importantly how to take care of yourself. Similarly, it is also essential for you to know the complications that can occur when high blood sugar levels are left unchecked for a long time. Some examples of short and long-term health complications include hypoglycaemia (very low blood sugar levels), heart disease, nerve damage, vision problems and even amputation.
This article is meant to serve as a ready reckoner for all possible Diabetic Complications so that you can see or spot the first symptoms coming from a mile away.
Here are 12 ways to Avoid and Prevent Diabetes related Complications.
- Have Carbs, but choose which ones: Your body needs carbohydrates and just because you have diabetes, doesn't mean you need to cut them out entirely! Instead, you should choose foods whose carbohydrate content breaks down slowly and gradually giving you a steady source of energy. Don't fret! There's a wide variety of such foods, including fresh vegetables, fruits (even sweet ones), whole grains and nuts, Remember, it is vital that for you to eat the right amount of carbs in each and every one of your meals.
- Lose Weight if needed: If you are overweight, dropping just a few kilos can visibly improve your body's ability to absorb insulin. Start with a basic weight-reduction plan (unless you have a very high BMI and/or your doctor/coach recommends otherwise). By losing weight, not only will you be able to improve your sugar levels and see a reduction in your blood pressure and body fat but also notice that you suddenly have more energy! Cutting out extra fat, sugar, and calories from your diet will have a positive long-lasting impact on your overall health.
- Sleep Well: Are you sure you're clocking in adequate Zzzz's? Scientists say that on an average, you ideally need between Seven and Nine hours of quality sleep every night. Not getting enough rest or oversleeping can have adverse effects on your body. For example: Too little or too much sleep can trigger a domino-like effect by - increasing your appetite - making you crave high-carb foods - causing weight gain and finally leading to risk of heart disease. Which is why you should get any sleep disorders like sleep apnea treated as that will improve your sleep quality and also help lower your blood sugar levels.
- Exercise: Be active. Even 10 - 15 mins a day is a good start and slowly build up to the level where you can yourself see and feel the benefits substantially. It also doesn't matter how or what you do. All that matters is that you get moving. Walk, skip, jump, climb, dance, cycle, march or just stand up and pace around your office or room every time you get a phone call. Exercise not only alleviates your stress levels, but also lowers your blood pressure, cholesterol and risk of heart disease. The icing on the cake here is that - with exercise, you may even be able to cut back on diabetes medication and possibly forever!
- Monitor your Blood Sugar regularly: Make it a part of your daily routine, like brushing your teeth! Checking your blood sugar levels has multiple benefits - it can caution you about the various symptoms indicating diabetes complications, it helps you in taking early action to avoid or reduce symptom severity, it helps you see the effects that different activities and foods have on your sugar levels, it gives you information about whether a specific treatment plan is working for you. Finally, it will show you how much you have progressed in your journey and where you stand in terms of reaching your ultimate target or goals.
- Manage Stress: Stress sends your body into a panic mode. This makes your stress hormones shoot up and insulin levels fall down. As you already know, insulin is the key hormone needed to keep your sugar levels stable. But in this case, insulin drops down and causes your blood sugar to rise. That's why you should try to avoid getting physically or mentally stressed. You can learn simple techniques to deal with your stress and try relaxation methods like breathing exercises, meditation, and yoga.
- Minimize Salt intake and Junk Food: Cutting down your salt intake helps in lowering your blood pressure and protects your kidneys. It's important to understand that it’s not enough if you just avoid adding extra salt to your cooking or when you're eating. Did you know that a major portion of salt you eat comes from the processed food you consume? Processed food is just another name for what we call ‘junk’ food. It has no nutritional value and contains huge amounts of sodium, sugar, and saturated fats. Some examples of processed or junk foods that you may be consuming without knowing it include ready-to-eat products, processed or cured meats. processed cereals like cornflakes, ketchup and other sauces, chips, snacks. and many other things that all of us love to have. It is recommended that you avoid processed foods altogether or at the least try to consume as little as possible. For those of you over 51 years of age, or having diabetes, high BP or kidney disease, it is highly advised that you fully and completely avoid all salt and try seasoning your food with spices and herbs instead.
- Don't neglect your cuts and bruises and ensure they heal well: Diabetes is sneaky. It raises your risk of infection and slows down healing. If you get hurt, clean the open wound with an antiseptic, treat it with an antibiotic cream and a sterile bandage. Show it to a doctor if it does not heal normally. Keep an eye on your feet every day
- Stop Smoking: Studies have shown that a diabetic smoker has double the risk of early mortality or reduced lifespan when compared with a diabetic non-smoker. By quitting smoking, you can lower blood pressure, risk of stroke, kidney disease, heart attack, and nerve damage. It is advisable to seek professional help to quit tobacco.
- Choose and include Superfoods in your diet: Customize your diet to - Avoid all saturated fat and trans fats. Choose mono and polyunsaturated fats like olive oil. Make superfoods your staple. Berries, fish, dark green leafy vegetables, sweet potatoes are perfect. You'll surely enjoy them!
- Communicate with your doctor and personal coach regularly: Consult your doctor at least once a month and your personal coach even more frequently to keep track of your health and successfully manage your condition. Get your Hb A1c levels checked once every 3 months and take your doctor and coach’s support in reducing your medication or insulin dosages. Get an annual or biannual dental check-up along with a physical examination to screen for eye, nerve, and kidney damage.
- Take care of your Heart: Diabetes could lead to heart disease. Make sure to get your ABCs checked regularly.
- A: A1C Level -The average of your blood sugar level over three months. Consult your doctor for target levels.
- B: Blood Pressure -Your goal should be below 140/80 Hg. Check it regularly!
- C: Cholesterol - Your goal for LDL should be 100mg/dl or less, and HDL should be above 40mg/dl in men and above 50 in women & Triglycerides should be below 150mg/dl.
Bottom Line
Now that you are well-prepared, it's time to take back control and make use of the 12 tips listed above by recognizing, avoiding or all together preventing any complications arising from high blood glucose levels. Reach out to your doctor and personal coach to get your customized treatment and nutrition plan at the earliest.
Improve Cardiovascular Health in Diabetes through 7 Lifestyle Changes
People with diabetes are more likely to have other conditions that raise the risk for heart disease and diabetes has long been considered a “cardiovascular risk equivalent. CHD risk equivalent means that a person will have a risk of >20% to develop a major coronary event (myocardial infarction + coronary death) over 10 years. It has been seen that people with T2DM without coronary heart disease (CHD) events showed a similar coronary mortality as non-diabetic patients who had a previous coronary event. Having both high blood pressure and diabetes can greatly increase your risk for heart disease.
What are the lifestyle changes that help in reducing the risk of heart disease in diabetics?
It is well known that lifestyle changes definitely benefit people with prediabetes and T2D. The American Heart Association (AHA), published 'Life's Simple 7' which are the seven risk factors that people can improve through lifestyle changes to help achieve ideal cardiovascular health. They are-
- Smoking Status
- Physical Activity
- Weight
- Diet
- Blood Glucose
- Cholesterol
- Blood Pressure
The great news, folks, is that research shows that people who maintain at least 5 of these factors at the ideal level can reduce the risk of diabetes by 70% and of heart attack, stroke, and heart failure leading to cardiovascular death by a gratifying 80%! Additionally, following these healthy lifestyle choices results in creating positive changes in prediabetes and T2D individuals as well. As the doctors say -
Healthy people need to work to stay healthy
So what are the 7 Lifestyle and Metabolic Health Goals you should strive for?
Whether you have Prediabetes or Type 2 Diabetes, following these lifestyle choices, will put you on the road of taking control of a potentially scary health scare.
- Manage and keep BP and Stress under Control: Maintain your Blood Pressure at 120/80 mm Hg or as your doctors recommends.
- Control Cholesterol: Choose foods with a low glycaemic index (GI) and GL. and aim for a total cholesterol level below 200 mg/dL
- Reduce and Monitor your Blood Sugar Levels: Keep your HbA1c (the average measure of your blood sugar over the past three months) below 5.7% if you have prediabetes and under 6.5% if you have T2D.
- Get Active & Exercise regularly: Regular exercise can help you get to and maintain a consistently moderate weight and increase insulin sensitivity. Your goal is 2 hours a day for a healthy heart!
- Eat Better, Eat Healthy: Replace processed carbohydrates with whole-grain foods, and increase the portions and variety of vegetables and other foods high in dietary fibre, and your home! This translates to about 4.5 cups of vegetables and fruits per day. Also, drink water and stay hydrated.
- Lose Weight: Keep a strict portion control. You should aim for a Body Mass Index (BMI) of less than 25. Lose weight gradually, and you will be able to achieve a healthy body mass index.
- Stop Smoking: You’ll reap cardiovascular benefits and also reduce your risk for cancer, COPD, and much more.
Bottom Line
Whew, this is a rather intense list of activities to follow and keep track of! But as they say No pain, No gain! So, imagine the dividends these efforts will yield. The biggest silver lining is that many research studies have independently endorsed these choices and goals. If followed diligently and maintained, these lifestyle choices are bound to reward you with excellent health and happy life!
Prevent, Delay and Reverse Diabetes through Lifestyle & Dietary Changes
Type 2 diabetes affects millions of people worldwide, and there are many more who are prediabetic. The prediabetic population has a high risk of having diabetes sooner or later. Diabetes brings a long list of complications such as kidney disease, hypertension, cardiovascular risk, and several health issues with it that can turn out to be lifelong. Whether you have Prediabetes or Type 2 Diabetes, there is now ample evidence from several research studies that by making a few healthy food changes, being physically active, and maintaining an ideal weight, it is possible to prevent, delay the onset of and in some cases even reverse Diabetes.
What is Prediabetes and Type-2 Diabetes
Prediabetes is a health condition where you have higher than normal blood sugar levels but not as high as in diabetes. Most of the time, you have no signs or symptoms, and it goes undetected until you develop Type-2 Diabetes. Being Prediabetic also increases your risk of getting heart disease, and stroke.
In Type 2 Diabetes, the cells of your body become resistant to insulin and are unable to absorb the sugar or glucose in your bloodstream for their energy needs. In addition to this, the insulin secreted by your pancreas is ineffective and unable to control the growing blood sugar levels, which results in constant high blood sugar.
Synopsis of Research Study
The Indian Diabetic Prevention Program Study of 531 middle-aged, overweight adults with impaired glucose tolerance and having primary risk factors of family history, age, and obesity. The study participants when put on decreased fat, complex carbohydrates, increased dietary fiber intake and lifestyle changes showed promising results with a significant reduction in risk and prevention of type-2 diabetes. Here are a few Recommendations for Lifestyle & Dietary Changes to Prevent, Delay, and Reverse Diabetes
Lifestyle Modifications
- Physical Activity: Walk, run, jog, or join some physical activity for at least 150 minutes each week. Swimming, cycling, skipping can help you stay fit. You may also go for structured or supervised physical activities.
- Lose Excess Weight: Being overweight is a dominant factor for being prediabetes. Losing just 5 to 7% weight can substantially reduce your risk of developing diabetes.
- Manage Stress: Consult a coach who will help you manage stress levels and keep you motivated.
- Quit Smoking: Stop smoking. Smokers are 50% more vulnerable to Type-2 Diabetes
- Avoid Alcohol: Give up excess drinking habits to reduce the risk of Type-2 Diabetes
Dietary Modifications
- Practice Portion Control: Eat smaller food portions. You may also drink a glass full of water before meals so that you feel fuller
- Eat more Fruits and Vegetables: Such as spinach, broccoli, and peppers. Add leafy vegetables like fenugreek and fenugreek seeds to your diet. Choose fresh fruits or a handful of nuts as a snack.
- Use Whole Grains: They are rich in minerals, vitamins, and phytoconstituents, and fiber and help in managing sugar levels and aids digestion. Avoid processed carbohydrates and refined flours.
- Avoid Processed Meats: Get your proteins from fish, peas, nuts, lentils, seeds and nuts instead. Cottage cheese (paneer) is also a good source of protein for vegetarians.
- Avoid Sugary Drinks: They contribute to weight gain, increased blood glucose, and triglycerides. Drink fresh fruit juices instead of sweetened beverages or carbonated drinks. Choose water over these drinks. Have tea or coffee without loads of milk and sugar. Do not go for powdered drinks or any fortified drinks.
- Choose Healthy Fats: Such as the unsaturated fats in nuts, omega-3 fatty acids, and vegetable oils to keep type-2 diabetes at bay. On the other hand, Trans-fats abundantly present in baked food, fast food, fried food products, and margarine are harmful.
Bottom Line
Type-2 Diabetes is a global challenge. However, making incremental changes in lifestyle with healthy food choices can essentially work wonders. Talk to your Healthcare provider about your risks of being Prediabetes or Type 2 Diabetes and what you can do to prevent, delay the onset of and in some cases even reverse Diabetes.
Intermittent Fasting and Diabetes
Intermittent fasting (IF), is a dietary approach that involves interspacing planned periods of fasting with regular eating. It has recently become a health trend and popular to lose weight, improve metabolic health, and perhaps even extend your lifespan.
What is Intermittent Fasting (IF)?
IF is a diet regimen that involves a cyclic pattern of unrestricted eating and fasting (no food at all or considerable calorie reduction) at brief intervals and involving limiting food intake into to 4-6 h and extends the overnight fast from 12 to 18 or 20 hours. Studies about IF have shown that it helps in significant weight loss, improved fasting glucose levels, more tolerance and no hypoglycaemia. Hence it has been recommended as a beneficial additional dietary strategy for T2DM management.
What are 6 Types that Intermittent Fasting can be done?
- 16:8 Diet: The 16/8 method involves daily fasts of 14 to 16 hours a day, and limits you’re eating window to 8 to 10 hours. Within this time, you can consume two to three meals, as per preference. For example, if you eat your dinner at 8 pm and fast till noon the next day, your fasting window is 16 hours.
- 5:2 Diet: Involves eating 500–600 calories for 2 days out of the week and eating normally the other 5 days. For example, you eat regular meals every day except Tuesday and Friday. On your fast days, you eat small meals twice a day and keep your calorie intake limited to 500 to 600.
- Eat Stop Eat: Has one or two 24-hour fasts once or twice a week for example, if you eat your last meal at 8 PM on Monday and fast until your next meal at 8 PM on Tuesday, you have completed your fast for 24-hours.
- Alternate-day fasting: Fast every other day, either by not eating anything or only eating a few hundred calories. For example, you ate your last meal at 7 PM on Monday, did fast or limited calories on Tuesday, and again ate on Wednesday.
- The Warrior Diet: You eat small quantities of raw veggies and fruits all day, followed by a large dinner at night.
- Spontaneous meal skipping: You may skip your meals when you do not have time or are not hungry.
Here are some Important Pointers to remember if you have Diabetes and want to try IF
- Get in touch with your doctor regarding if you are adopting an IF diet plan. Even if you can do it, stick to what your doctor recommends to you with food or medications.
- Make sure you eat a balanced diet during your fasting and non-fasting windows. Include food items for all groups of food.
- Avoid eating more than enough during your eating window.
- Include food items that have a low glycaemic index because these get absorbed slowly.
- Make sure to eat fruits, veggies, and fresh salads during your fast window. These make you feel full while maintaining your blood glucose level.
- When you break the fast, avoid fried, fatty, and sugary food products. Try baked, boiled, or grilled items instead.
- Drink plenty of water.
- Do not forget to check your blood sugar levels frequently.
- If you see the signs of hypoglycaemia, break your fast as soon as possible and get back to your usual diet.
IF should not be done by
- Women who are pregnant or trying to become pregnant (extended fasting periods may throw off your menstrual cycle)
- Those taking diabetes medication (blood sugar can drop too far in the absence of food)
- Anyone on multiple drugs (food, or lack of it, can affect absorption and dosage)
The Bottom Line
Medical guidelines on how to manage therapeutic intermittent fasting in patients with diabetes are far and few. However, when done under the supervision of the patient’s healthcare provider, and with appropriate personal glucose monitoring, intermittent fasting can be safely undertaken in patients with diabetes.
The Hype about Glycaemic Index
If you are a health-conscious person who is pretty watchful of what all you eat and avoid, then you might be familiar with a much-hyped term called Glycaemic Index (GI). So, if you're wondering - is the entire scene around this Glycaemic index justified, or is it just another fad diet thing? Let's decipher the Glycaemic code!
What do you mean by Glycaemic Index?
Glycaemic Index is a grading system that classifies different carbohydrate-containing foods based on how quickly or how slowly those items can make your blood glucose levels spike. The lesser the GI numbers, the better. The reason - Low GI means a lesser impact on your blood sugar levels.
Glycaemic Index Grading
|
Glycaemic Index |
Grade |
Recommendation |
Food Examples |
|
55 or less |
Low |
Good to go |
Green Veggies, Raw Carrots, Fruits (Most) Lentils, Kidney Beans, Chickpeas |
|
56 to 69 |
Medium |
In Moderation |
Banana, Sweet Corn, Multigrain Breakfast Cereals, Raw Pineapple |
|
70 or More |
High |
Avoid |
Potatoes, White Bread, White Rice |
Decoding the GI Code
- Low GI Foods: The food items with a GI score of 55 or less contain good carbohydrates. These foods break down into glucose slowly and therefore get absorbed into your blood slowly. So, having these food items will not make your blood sugar level rise abruptly.
- Medium GI Foods: The food products with a GI score between 56 to 69 are medium GI foods. These contain carbs that convert into glucose a bit faster than that of low GI foods.
- High GI Foods: A GI score of 70 and more is a bit of a red signal. These contain carbohydrates that break down into glucose quickly, making your blood sugar shoot up all of a sudden.
Comparing these scores can help you choose healthier food options.
For Example - A muffin baked using refined flour has a GI score of 75, whereas a muffin made from whole wheat has a GI of 45. So, you be the judge of which one you should prefer. Whether you want to lose weight, control diabetes, or manage any other underlying lifestyle condition, choosing the right food with the right Glycaemic Index is crucial.
GI Score and its Limitations
- Glycaemic Index score does not reflect the actual quantity of any given food that you would eat. It is determined in line with 100 gm of food.
- For Example - The Glycaemic Index of watermelon is 80, making it a no-no fruit with high GI. However, the amount of digestible carbs in watermelon is relatively low in a standard serving. Simply put, to make our blood glucose level rise, you will have to munch on truck-loads of watermelon. How can you work through this? To accurately address this, you have to understand another term called Glycaemic Load or GL. Glycaemic Load is the numerical value relates to the rise in your blood glucose on eating a standard serving size.
- For Example - The GL score of 3/4th cup (120 grams) of watermelon is 5, making it a healthy food option. So, logically speaking, any food with a High GI and Low GL will NOT make your blood sugar level rise. So, you can have them without any stress.
2. It does not tell you anything about the rest of the nutritional value of a given food.
- For Example - The GI and GL of whole milk (250 ml) are 31 and 4, respectively. However, its fat content is high. Therefore, it does not make the right choice for people who are on a weight loss regimen.
Classification of Glycaemic Load follows the below pattern
Here is another chart with the GI and GL scores of some common food items
The Bottom Line
When we talk about GI, people have mixed reactions. Some call it hypes, while some others think it works. Choosing food items on the basis of GI or GL can help you reverse your diabetes and manage your weight provided you choose the right food because many food items that make the typical diet for weight loss contain food with low GI values. However, researchers also warn, that regardless of if you want to lose weight, maintain weight, or control diabetes, you should not use the GI factor alone. You should also consider other nutritional requirements, such as fat, protein, vitamins, minerals, ensuring a well-balanced diet. If you're still unsure about what foods to choose or not choose, get in touch with any of our expert nutritionists for an insightful overview of the choices available to you.
The Science of Diabetes Reversal
Diabetes is a chronic condition that has emerged as one of the growing health challenges in the 21st-century. Till very recently it was believed that Diabetes is a chronic, incurable disease that lasts your whole life. “Once a Diabetic, always a Diabetic.” The reality however is that, while diabetes is a serious condition, each individual has a unique representation in terms of causes, risk factors, type of diabetes and complications. Hence it requires personalized management tailored to target your specific needs and issues.
“A good life is a process and not a state of being. It is a direction not a destination”
Adapting this quote to reflect the present scientific advances made in the management of chronic care, a fitting interpretation would be that on the road to Diabetes, no matter how far you've travelled, you can always halt, turn around and return to living a healthy life.
Type 2 Diabetes is a progressive metabolic disorder, which means it doesn't appear overnight. It starts with small changes in your metabolism even long before it's diagnosed, and gradually worsens over time leading to a stage where your body is unable to self-regulate. This leads to an insufficient insulin secretion and build-up of sugar levels in your blood. Having high blood sugar levels is termed Hyperglycaemia and leaving it unmanaged or untreated leads to tissue damage in susceptible organs, resulting in T2DM and secondary complications that affect your eyes, kidneys, feet and heart health. Scary right? How one little thing like being at risk and not eating healthy can lead to you going blind, having a stroke or needing a limb amputation!
But wait! Silver Lining Alert! Evidence Based Studies have shown that it is possible to stop this progression and work towards successfully preventing and Reversing Type 2 Diabetes.
So, what is Diabetes Reversal?
“Diabetes Reversal” is a term that has found its way into the lexicons of scientific journals along with topping the list of most searched buzzwords for Diabetes or Obesity related Diabetes. But make no mistake, it deserves all the accolades coming its way and more. This breakthrough has given new hope to individuals with Type 2 Diabetes and Prediabetes of being able to get back to living a healthy, stress-free normal life.
How will you know if your Diabetes has been Reversed?
If you have been diagnosed with Type 2 diabetes (HbA1c >6.5%) and are able to show a significant improvement in insulin sensitivity for an extended period of time by bringing your HbA1c under the threshold of 6.5% without the use of any glycaemic control medications (Antidiabetic medications), you have successfully Reversed Diabetes. So yes! Diabetes can be reversed!
Does that mean you are now cured?
Although the words cure and reversal may seem contextually similar, they don't mean the same things. The term cure implies that the original pathophysiology or cause of the condition is completely eliminated and there is no chance of it recurring again.
For Example, | Last year, Mr. Rao was diagnosed with Atherosclerosis; a progressive cardiovascular disease that resulted from a build-up of fats and cholesterol in and on his artery walls. This plaque had gradually built-up to the point where it was now obstructing the blood flow to his heart, and required surgery. Mr. Rao underwent an Angioplasty and was fitted with a coronary stent. The surgery was successful, the blockage was removed and the stent holding up his arteries enabled that the blood flow to his heart was restored. Now Mr. Rao is back home, tending to his garden, playing with his grandchildren and back to living his regular life. But, does that mean Mr. Rao is cured.? While it's true that he has gotten back near-normal physiological function of his arteries, the pathology of his collapsed arteries still remains. So, if Mr. Rao does not follow a healthy diet and lifestyle needed to maintain his cholesterol levels, history will repeat itself, plaque will again start to build up and may now block the placed stent itself restricting blood flow yet again.
Similar to Atherosclerosis, Type 2 Diabetes is also a progressive condition, which develops over a long period of time, starting with insulin resistance. Consistent high blood sugar levels over time lead to your pancreatic beta cells becoming dysfunctional, causing irreversible damage to your tissues and susceptible organs. But Type 2 Diabetes can be reversed by restoring your blood glucose levels to a normal range again. This doesn't mean diabetes has gone for good, but it is now in your control to keep and maintain it at normal levels through a healthy lifestyle.
What is the scientific reasoning behind how Diabetes Reversal is achieved?
Before we go into the science behind reversal, let's take a step back, and think about the time when the sun shined bright, the skies were a clear blue and your Metabolism was great! Remember that? No? Then lets first brush up on the workings of your Carbohydrate Metabolism, and how it lost its way. Normally, your Blood Glucose, also called Blood Sugar, levels rise after you eat. Your pancreas then release insulin into the bloodstream, which then lowers your Blood Glucose back to normal range.
Here’s a simple illustration of how Carbohydrate Metabolism normally works.
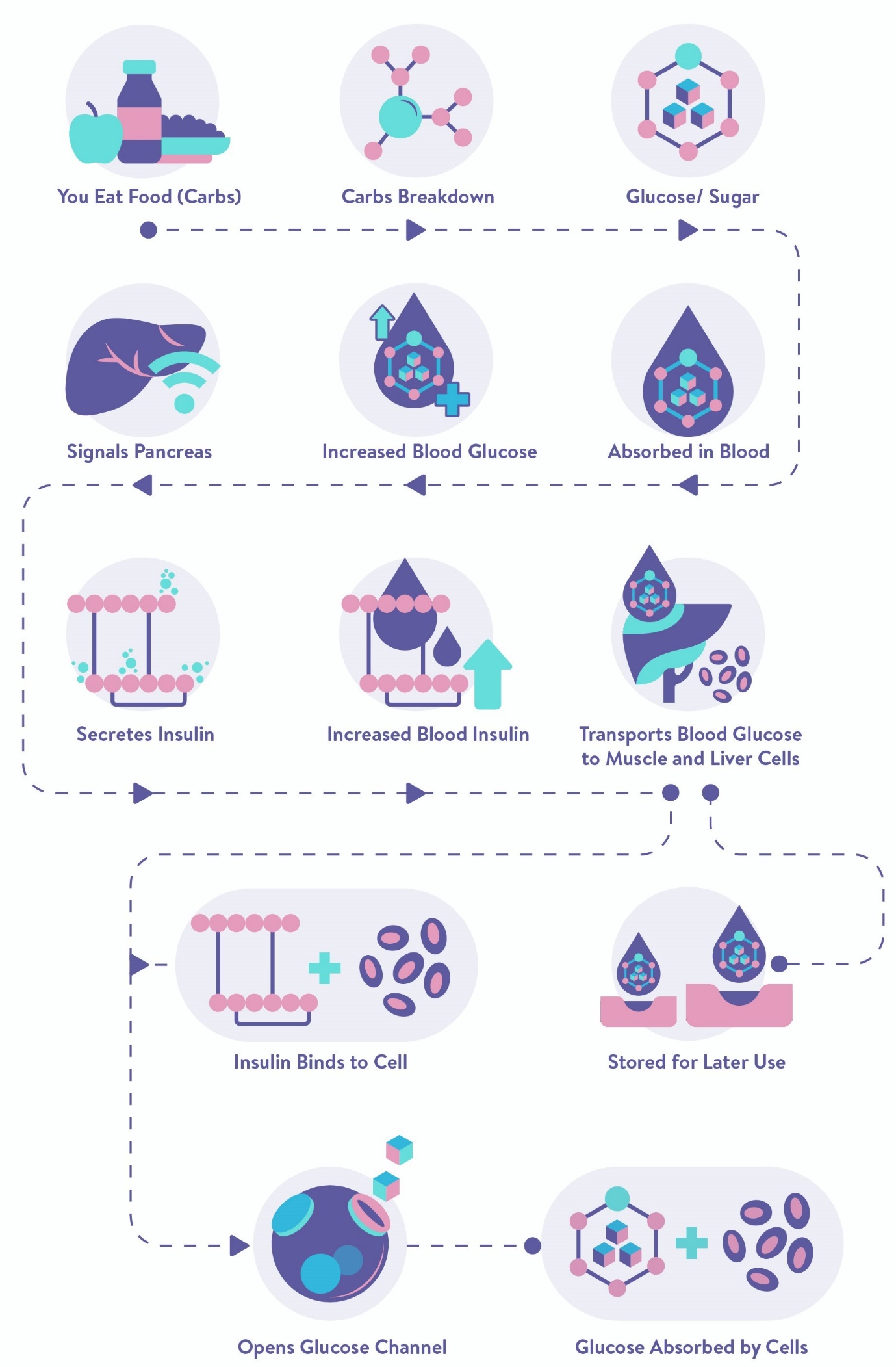
Fig 1. Metabolism of Carbohydrates into Glucose and Energy
So, what causes your metabolism to become disordered?
To understand Carbohydrate Metabolism in detail and what causes it to become disordered, check out our article Metabolism 101. A short version goes like this.
The hormone insulin helps control the amount of glucose or sugar in the blood. Insulin resistance is when cells in your muscles, body fat and liver start resisting or ignoring the signal that the hormone insulin is trying to send out—which is to grab glucose out of the bloodstream and put it into our cells. Hence, Glucose can't enter the cells as easily, and builds up in the blood and eventually leads to type 2 diabetes.
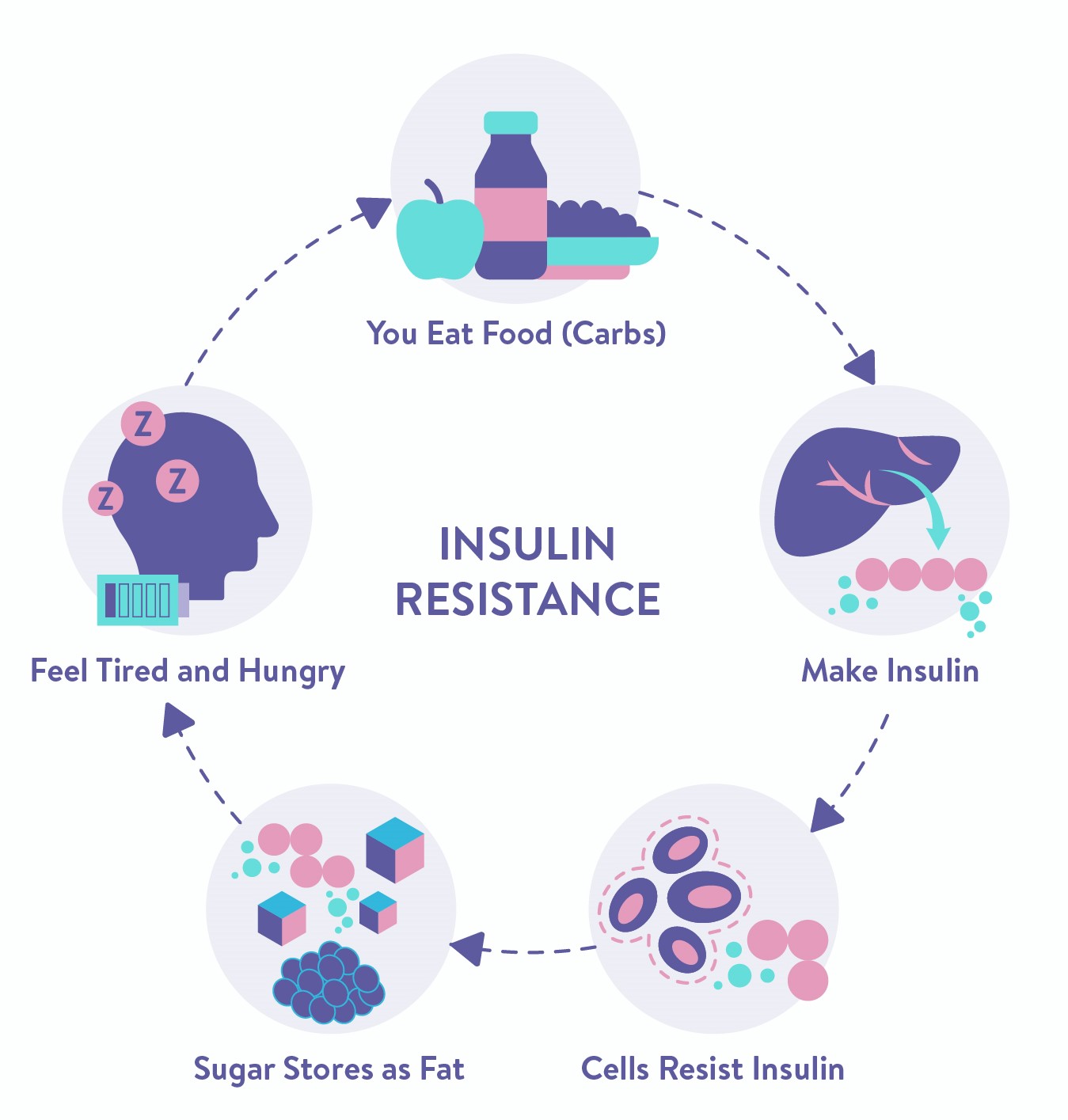
Fig 2. Vicious Cycle of Insulin Resistance
The vicious cycle of Insulin Resistance is like a tough maze; easy to get in but a struggle to get out of. Evidence Based Studies show that the only way obesity-related Type 2 Diabetes can be reversed, is by creating a break in this continuous cycle of Insulin and Glucose insensitivity. By doing this, you will be taking the strain off your insulin-producing cells, giving them a chance to recuperate and at the same time regulating your blood glucose levels by allowing your cells to absorb the energy they need.
To learn more about the causes, effects, prevention and management, check out our article on Insulin Resistance.
Now that you're all caught up with the basic workings of your Metabolism and Insulin Resistance, you finally know how your bright happy days took a dark turn and led you down this scary tunnel called diabetes. But like we said before, don't fret! We see a light at the end of this tunnel - and it's getting brighter. But how? In a nutshell, you need to target all the factors causing the Insulin Resistance, and make your cells responsive to insulin again. Does that seem like something that's easier said than done? Fortunately, it's not, and can be achieved by following Seven Essential Practices that are backed by evidence-based studies and endorsed by authorized health agencies worldwide.
Presenting the Dr. Wealthify Super Seven!
The Dr. Wealthify Super Seven is a set of Seven curated interventions, cherry-picked from clinical trials and published research studies, that have been tried, tested and proven to be effective in reversing diabetes. Let's examine them individually to understand what each one of them entails.
1. Dietary Interventions
Studies have shown that an effective and sustainable way to reverse Diabetes is by taking a Complex Carb counted, Portion appropriated and sustainable (lifelong) balanced meal plan. This entails consuming a nutrient dense diet, that's rich in fiber and resistant starch. Remember to stay away from generic one-size-fits-all diet plans on the internet and say No to fad diets, processed food sand calorie counting! You are unique and deserve a diet plan that's customized to your preferences and requirements.
2. Progressive Fitness Interventions
The benefit of exercise in improving the metabolic disorders of Type 2 Diabetes is well established. Studies show that metabolic disruption, including insulin resistance and dyslipidaemia, stems from alterations in free fatty acid metabolism and is caused by truncal or abdominal obesity. Strength training should be included as part of your weight loss regimen (as required), but it can also be paired with working towards a lean body mass, which has been independently associated with improved insulin sensitivity. Confused about which one to pick? That's where we come in. You need a fitness plan that's progressive and safe for all forms of physical activity. A tailor-made plan consistent with your desires, goals, age, comfort levels and highly effective for the long-term management of Type 2 Diabetes
3. Blood Glucose Monitoring
Blood Sugar Monitoring (BGM) is often called the cornerstone of effective diabetes management. Testing is the only way you can be confident about knowing what your blood glucose levels are at any given time. Regular monitoring is crucial because it gives you enough and more information to be able to manage your blood sugar levels and keep them in check. There are 2 ways your blood sugar levels can be monitored –
a) Self-Monitoring Blood Glucose Monitoring (SMBG)
- Glucose monitoring devices that you will use to check your glucose levels in seconds using only a small drop of blood. usually obtained from pricking your finger with a lancing device and gives measurement of your blood glucose level at a given time
b) Continuous Blood Glucose Monitoring (CGM) - Provides information
- To your provider to adjust or lower your medication.
- To identify high and low levels before serious problems like Hypoglycaemia can develop.
- To see and understand the trend of your average blood sugar levels over a period of time. This gives you a positive boost when you see how well you have been managing your sugar levels.
- Tell you how well you are balancing your medications, insulin therapy, meal planning, and exercise to manage your diabetes.
To learn more about CGM and its benefits, check out our article on A Starters Guide to Continuous Glucose Monitoring (CGM) and Low-Sugar Optimal Diet Through CGM
4. Short-term compliance to medication to reduce long-term dependency
The struggle you're going through today is developing the strength you need for tomorrow.
The World Health Organization (WHO) in its 2003 Medication Adherence Report states that adhering to a prescribed treatment is an investment that provides significant and positive returns through primary prevention of risk factors and secondary prevention of adverse health outcomes. T2DM is a progressive disease and, along with diet and exercise, pharmacological therapies are needed to sustain glycaemic control and reduce complications.
Diabetes Reversal starts with taking strain off your overworked pancreas to give them a reprieve, some rest, and a chance to heal from the damage caused by high sugar levels so far. The fastest and most efficient way to reduce and normalize your blood sugar levels is through medications. When you skip or stop taking your medications, you are giving up any and all control you have over your blood sugar levels. Left to its own devices, the glucose starts accumulating in your blood and rapidly increasing blood sugar to toxic levels., causing your pancreas to continue producing ineffective insulin until the beta cells wear out and stop functioning. Unfortunately, the damage caused is permanent and irreversible. Since your beta cells cannot be revived anymore, you will have to be put on insulin therapy for life. Compliance in taking your medication regularly now, is quintessential to avoid adverse outcomes and life-long dependency in the future.
5. Weight Loss
Lifestyle modification has long been hailed as being the foundation of Weight Loss; greater the loss, greater the clinical improvement seen. Did you know that weight reduction with lifestyle interventions has been shown to reduce the incidence of diabetes by 58%? Abdominal obesity (belly fat) is a major driver in the development of diabetes and cardiovascular disease. Weight reduction, therefore, is a key therapeutic goal in both the prevention and management of Type 2 Diabetes. Studies show that even a loss of 5–10% of body weight can improve fitness, reduce HbA1c levels and improve cardiovascular disease (CVD) risk factors. Additionally, it can reduce your medications not just for diabetes, but also those used to lower hypertension and high cholesterol.
6. Mindful Habits
“We are what we think, and all that we are arises with our thoughts.” Gautama Buddha
Living with diabetes requires significant adaptation and coping skills. Chronic stress and negative emotions are strong risk factors for development of obesity, diabetes, hypertension and cardiovascular disease. Practicing Mindfulness-Based Stress Reduction along with lifestyle modification and pharmacological management leads to improvement across all domains of holistic care – biological, psychological and social. Several studies show that having a positive attitude and reducing your stress levels contributes to modest improvements in body weight, glycaemic control and high blood pressure in individuals with diabetes.
7. Essential Awareness and Self-care
Studies show that the way an individual responds to challenges has an impact on their clinical outcomes. With Diabetes, the associated challenges are dynamic and change over time, making it essential to develop good problem-solving skills to cope with emerging issues. When you have Prediabetes or Diabetes, you may go through a myriad of feelings that take a toll; both physically and emotionally. Acquiring skills and healthy coping techniques make you aware enough to recognize these emotions as normal and take steps to reduce the negative impact they have on your overall wellbeing. By being aware of the pitfalls, what they are and how they manifest, you can make informed choices, decisions and take the necessary actions to reduce your risk of developing diabetes-related complications.
What happens in the Journey from Start to Reversal?
- Step 1: Reduction/Normalization in Blood Sugar but The Medication (If Any) Remains the Same.
- Step 2: Reduction in Both Blood Sugar and Medicines (If Any).
- Step 3: Hba1c (%) Is More Than 6 And the Medication is Reduced
- Step 4: Hba1c (%) Is More Than 6 And the Medication Has Stopped.
- Step 5: Hba1c (%) Is Less Than 6 And Medication Has Stopped.
- Step 6: Hba1c (%) Is Less Than 6, Medicine Has Stopped and Improved Insulin sensitivity.
- Step 7: Blood Sugar Remains Normal Irrespective of Dietary fluctuations (Excellent Fitness).
Bottom Line
The path to Diabetes Reversal can be demanding and overwhelming, so the first step is believing it's possible! Start by learning about the why’s, what’s and how’s of your condition. Recognize that Insulin is your friend; who has, and still continues to work tirelessly to make sure you never run out of energy. Right now, he needs you to take a stand, show that you have his back and help him get back to his glory days. Like all good things in this world, this doesn't come easy. It requires time, patience, commitment and perseverance to stay and continue on the right track. There will be times when your friendship is tested and you may feel tempted to just give up, but remember, the fate of your friend is in your hands. Ironically, you choosing to take a path of least resistance, affects your friend inversely by making your cells even more resistant to insulin and can keep him locked out forever. So, stay positive and remember anything that's worth doing, should be done well. To find out more about your path back from diabetes.